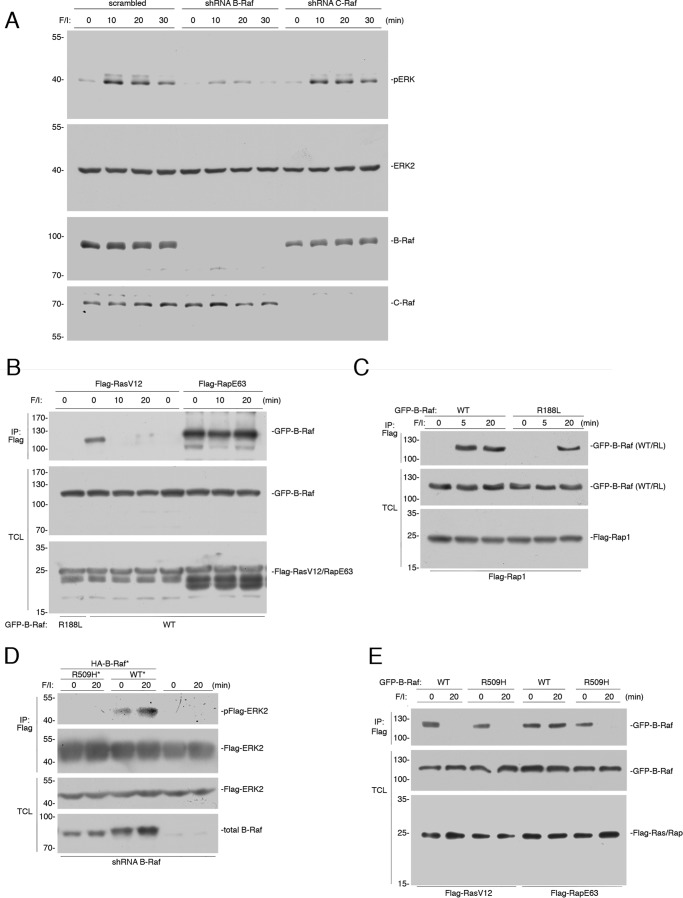
FIGURE 1.
B-Raf binding to Rap1 following cAMP stimulation is indirect. A, HEK293 cells were transfected with scrambled shRNA, or shRNA against B-Raf or C-Raf, as indicated. A, HEK293 cells were treated with F/I for 0, 10, 20, and 30 min. The endogenous levels of pERK and total ERK2, and the efficacies of the shRNAs are shown. B, cells transfected with wild type GFP-B-Raf (WT) or GFP-B-Raf R188L (R188L) and either FLAG-RasV12 or FLAG-RapE63 were treated with F/I for the indicated times. The presence of GFP-B-Raf following FLAG immunoprecipitation (IP) was detected by Western blotting (upper panel). The levels of FLAG-RasV12/RapE63 and GFP-B-Raf in the TCL are shown in the lower two panels. C, cells transfected with FLAG-Rap1 and wild type GFP-B-Raf (WT) or GFP-B-Raf R188L (R188L) were treated with F/I, as indicated. The presence of GFP-B-Raf following FLAG IP was examined. The levels of transfected proteins in the TCL are shown. D, wild type B-Raf, but not B-Raf R509H, can rescue cAMP activation of ERKs in cells depleted of B-Raf. HEK293 cells that were stably transfected with shRNA against B-Raf were transiently transfected with FLAG-ERK2 and either GFP-tagged vector control, shRNA-resistant (*) wild type B-Raf (WT*), or the R509H mutant (RH*) as indicated or vector (not shown), and treated with F/I as indicated. Phosphorylated FLAG-ERK2 was detected within the FLAG IPs (pFlag-ERK2). The levels of FLAG-ERK2 and endogenous B-Raf within total cell lysates (TCL) are shown. E, cAMP activation of ERKs by Rap1 requires B-Raf dimerization and KSR. HEK293 cells transfected with wild type GFP-B-Raf (WT) or GFP-B-Raf R509H (R509H), and either FLAG-RasV12 or FLAG-RapE63 were treated with F/I, as indicated. The presence of GFP-B-Raf following FLAG IP and the levels of transfected proteins in the TCL are shown.