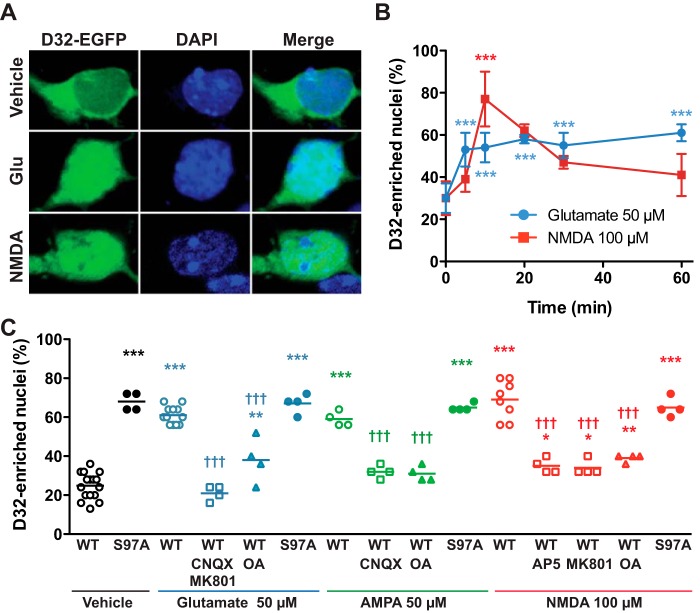
FIGURE 7.
Glutamate induces nuclear accumulation of DARPP-32 in cultured striatal neurons. A, representative confocal images of striatal neurons in culture transfected with DARPP-32 fused with EGFP (D32-EGFP) treated for 10 min with vehicle, glutamate (Glu, 50 μm) or NMDA (100 μm). B, time course of the effects on nuclear DARPP-32, as in A, of glutamate (50 μm) or NMDA (100 μm) for the indicated times. Data are the means ± S.D. (n = 2–7 independent cultures with at least 25 transfected cells counted). One-way ANOVA: glutamate, F5,16 = 17.02, p < 0.0001; NMDA, F5,11 = 12.09, p = 0.0004. C, neurons were transfected with wild type DARPP-32-EGFP (WT) or D32-EGFP containing a Ser-97 to Ala mutation (S97A). Glutamate-induced DARPP-32 nuclear translocation was prevented by incubating striatal neurons in culture with an AMPA receptor antagonist (CNQX, 10 μm), NMDA receptor antagonists (MK801, 10 μm; AP5, 50 μm), or a PP2A inhibitor (okadaic acid (OA), 500 nm), 40 min before the addition of glutamate (50 μm), AMPA (50 μm), or NMDA (100 μm) for 10 min. One-way ANOVA: F14,68 = 53.7, p < 0.0001. In B and C post-hoc analysis was done with Newman-Keuls test. *, significant differences with time 0 (B) or WT/vehicle (C). †, significant differences with WT/respective agonist (glutamate or AMPA or NMDA) alone (C). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; *** and †††, p < 0.001.