Figure 2.
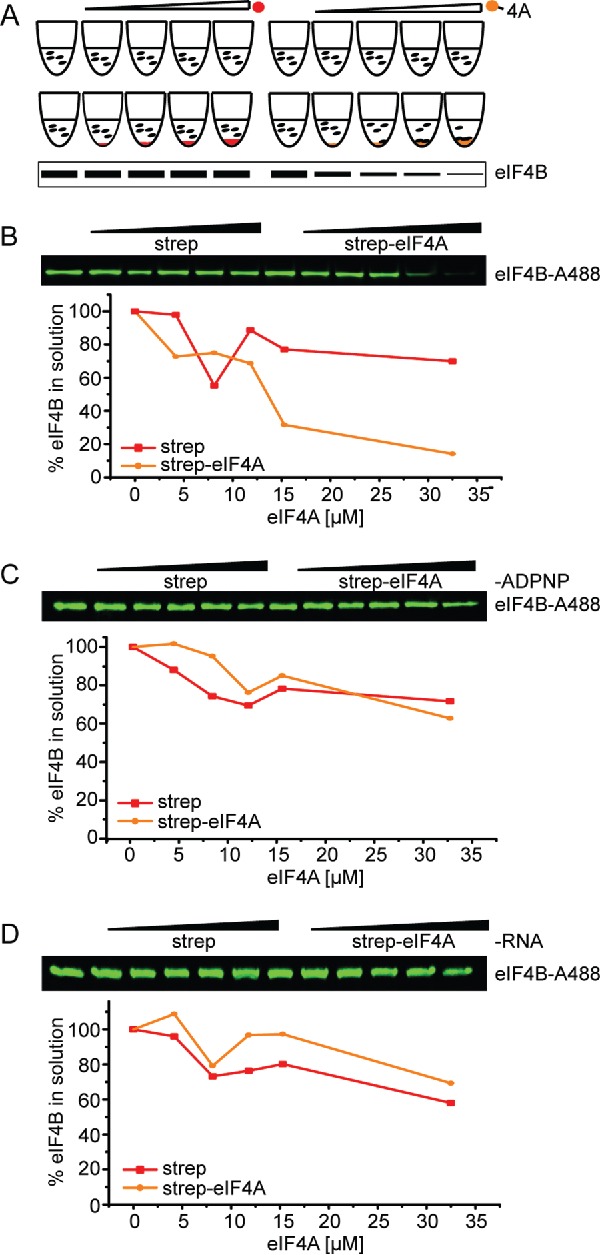
eIF4B binds to eIF4A in the presence of ADPNP and RNA. (A) Schematic overview of the supernatant depletion assay after Pollard et al.22 to probe binding of eIF4B to eIF4A. Increasing amounts of streptavidin beads with immobilized biotinylated eIF4A (eIF4A-bio, orange sphere) or without (negative control, red sphere) were incubated with a constant concentration of eIF4B or Alexa-488 labeled eIF4B (eIF4B-A488). The supernatant is analyzed by SDS-PAGE. A decrease of protein in the supernatant reflects binding to eIF4A-bio. (B) Supernatant depletion assay to follow binding of 0.25 µM eIF4B-A488 (eIF4B_248C/274C) to eIF4A-bio in the presence of 5 µM RNA (32mer) and 10 mM ADPNP (Coomassie Blue staining). eIF4A-bio concentrations are 0, 4, 8, 12, 15 and 33 µM. eIF4B in the supernatant was quantified from the fluorescence intensity. Red: depletion upon addition of streptavidin beads (negative control), yellow: depletion upon addition of eIF4A-conjugated streptavidin beads. Data shown are a representative example of two independent experiments (see Fig. 3C). (C), (D) Supernatant depletion assay with eIF4B in the absence of ADPNP or RNA.
