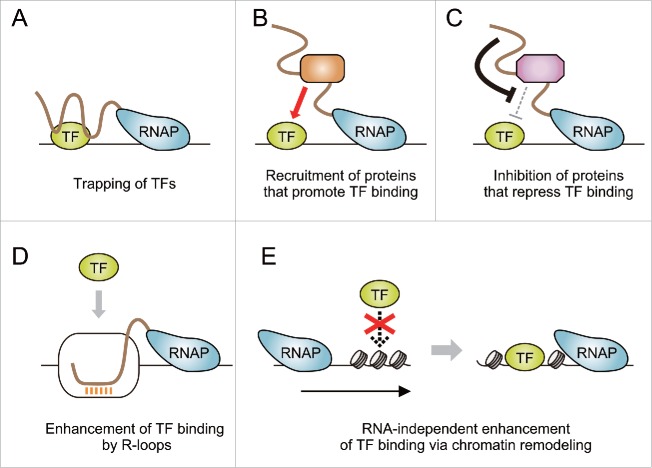
Figure 2.
Possible models for how TF binding is driven by on-site transcription of ncRNAs. (A) Nascent ncRNAs trap TFs at their target DNA regions. (B) ncRNAs recruit proteins that assist TF binding (e.g., histone modifiers and chromatin remodelers that create open chromatin structure). (C) ncRNAs attenuate functions of proteins that play inhibitory roles for TF binding (e.g., corepressors that establish chromatin states refractory to TF binding). (D) ncRNA transcription leads to the formation of R-loops that facilitate TF binding. (E) Transcription-coupled chromatin reorganization promotes TF binding independently of RNA products.