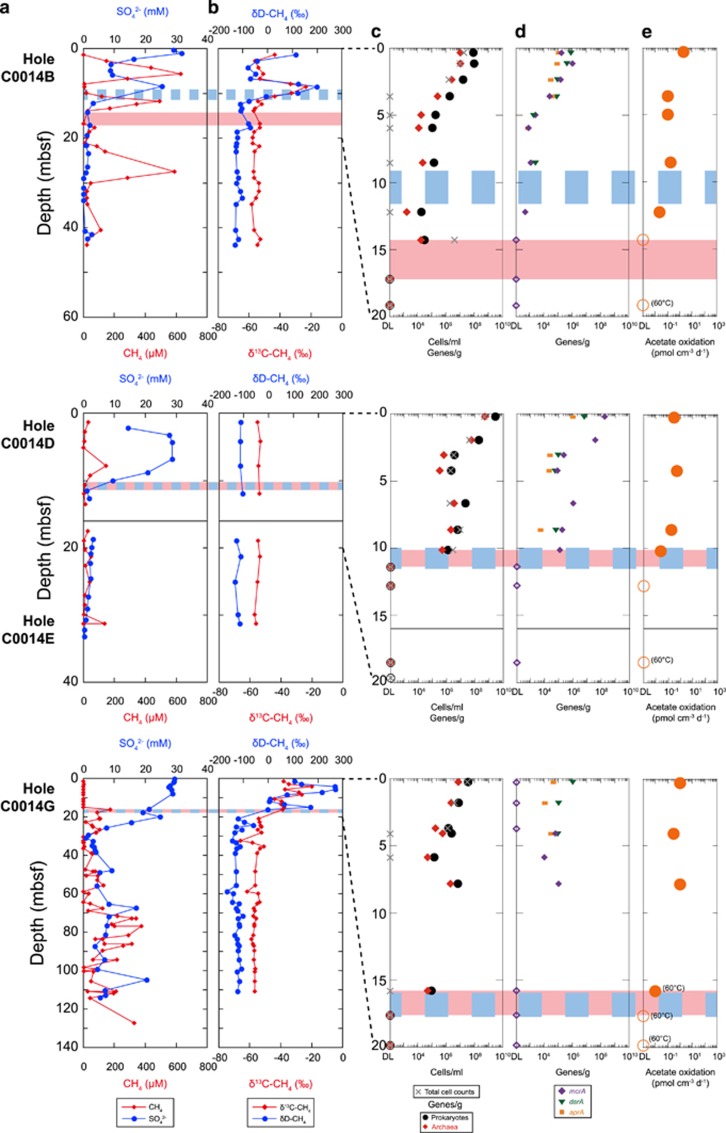
Figure 1.
Pore-water concentrations of methane and sulfate (Takai et al., 2011) (a), the carbon and hydrogen isotopic composition of methane (b), the numbers of 16S rRNA and functional genes (c and d) and heterotrophic activity (e) in the subseafloor core samples at IODP Site C0014. Q-PCR was used to quantify numbers of 16S rRNA genes of prokaryotes (black circles) and archaea (red diamonds), and functional genes of mcrA (purple diamonds), dsrA (green triangles) and aprA (orange squares). The total cell counts (gray crosses) were originally reported by Takai et al. (2011). Heterotrophic activity was determined based on the potential activity of the anaerobic oxidation of acetate. The incubations were conducted at 30 and 60 °C based on the in situ temperatures in Supplementary Figure S1. The samples incubated at 60 °C were indicated with parentheses, next to each symbol. Values below the detection limit for the Q-PCR data and heterotrophic activity are plotted as open symbols on the left axes. The red-shaded layers indicate the depth range of the limits for microbes based on Q-PCR data and heterotrophic activity. These depth ranges correspond to the depths of 14.3–17.2 mbsf in Hole C0014B, 10.2–11.4 mbsf in Hole C0014D and 15.8–17.6 mbsf in Hole C0014G. The possible impermeable layers in Supplementary Figure S2 are indicated by the blue dashed lines.