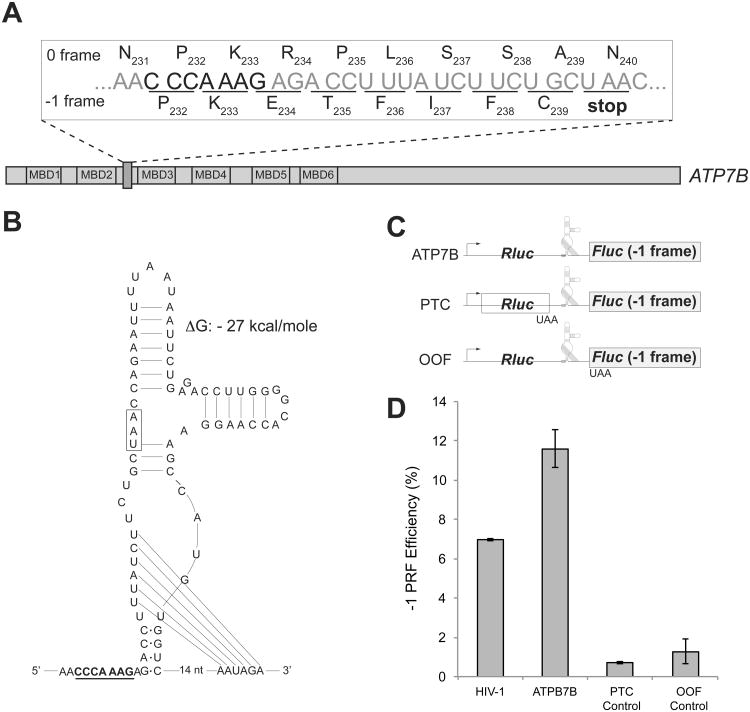
Figure 6. -1 PRF element within the human copper transporter ATP7B gene.
(A) The location of the heptameric CCCAAAG SS of the human ATP7B gene. Translation in 0 frame generates the full-size ATP7B copper transporter; slippage of the ribosome into -1 frame (underlined codons) would cause termination of translation at the 240th codon (UAA) and result in production of a truncated protein consisting of the first two MBDs of ATP7B.
(B) The ATP7B mRNA segment downstream of the slippery sequence could fold into a PK. The SS is underlined and the -1 frame stop codon is boxed.
(C) The dual luciferase reporter constructs used to test efficiency of -1 PRF directed by the ATP7B SS. The minimal ATP7B sequence including the SS and the putative PK structure was inserted between the Rluc (0 frame) and the Fluc (-1 frame) genes. The premature termination codon (PTC) control construct carried a stop codon at the end of the Rluc gene. The out of frame (OOF) control construct contained a stop codon at the beginning of the -1 frame Fluc ORF.
(D) The -1 PRF directed by the HIV-1 PRF signal in comparison with the ATP7B PRF element within the constructs shown in panel (C) expressed in HEK293T mammalian cells. The errors bars represent standard deviation from the mean based on at least 6 independent replicates.
See also Figure S4.