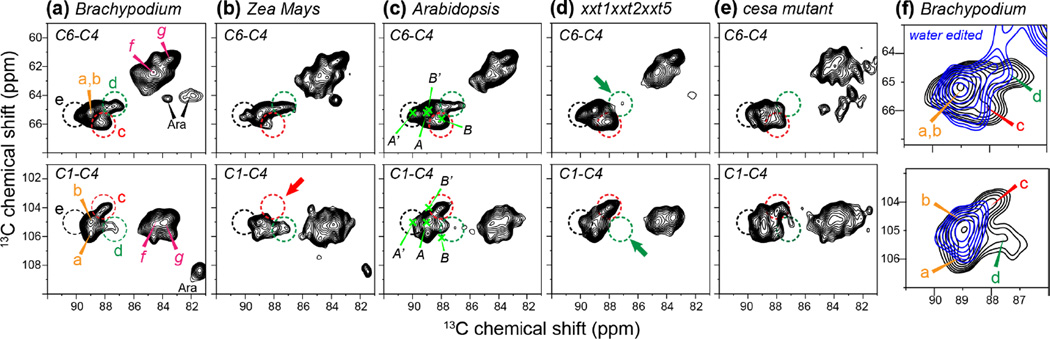
Figure 3.
Comparison of the cellulose C6-C4 (top row) and C1-C4 (bottom row) of the 2D PDSD spectra of various primary cell walls. (a) Brachypodium cell wall. (b) Zea Mays cell wall. (c) Arabidopsis cell wall. (d) xxt1xxT2xxt5 mutant Arabidopsis cell wall. (e) CESA mutant Arabidopsis cell wall. Dashed circles guide the eye for the five types of interior cellulose and two types of surface cellulose chemical shifts. (f) Water-edited 2D PDSD spectrum (blue) of the Brachypodium cell wall, superimposed with the full PDSD spectrum (black). Cellulose a and b signals are retained while interior cellulose c and d signals are suppressed in the water-edited spectrum, indicating the different hydrations of these cellulose structures.