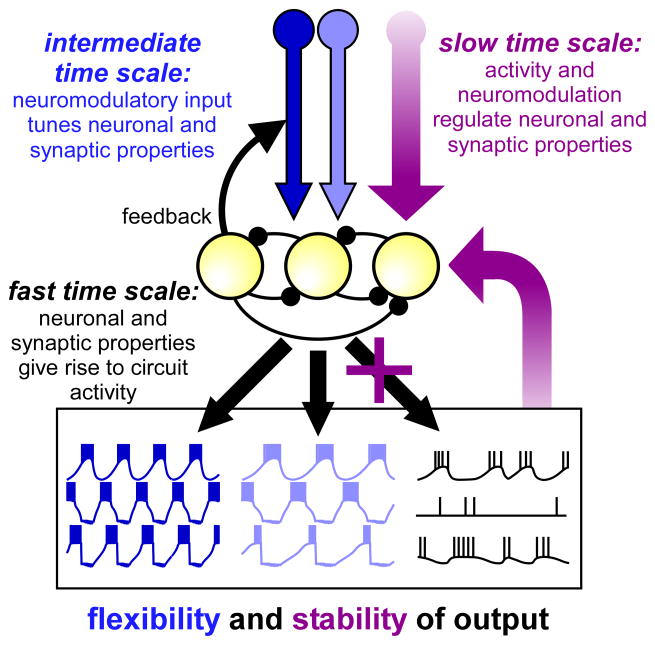
Figure 3.
Schematic of interactions of different regulatory mechanisms that affect circuit operation at different time scales. At the fast time scale, neuronal and synaptic properties give rise to circuit activity. At the intermediate time scale, neuromodulators convey flexibility, as different neuromodulators can tune neuronal and synaptic properties to generate different circuit outputs. Circuit activity itself can shape input patterns from modulatory neurons through feedback connections. At the slow time scale, long-term regulatory mechanisms dependent on neuronal activity and the presence of neuromodulators convey stability of circuit output and prevent circuit crashes.