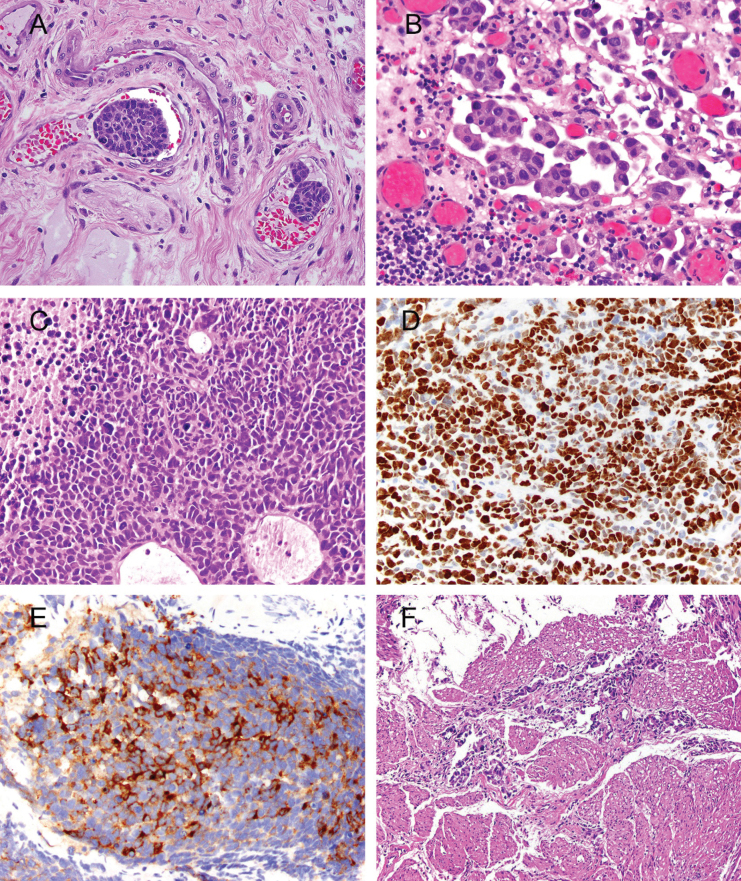
Fig.1.
Photomicrographs illustrating histopathologic features that are important for clinical risk stratification. A. Lymphovascular invasion; H&E, 40x. Cancer emboli are seen in two vessels. Spaces surrounding cancer cells are disproportional by size and shape, have proteinaceous material and red blood cells, and are lined by endothelium. B. Micropapillary invasive urothelial carcinoma; H&E, 40x. Lacunae with multiple micropapillae are considered to be the most reproducible microscopic feature. C. Small-cell carcinoma; H&E, 40x. Solid sheets of high grade cells with scant cytoplasm, frequent mitoses, apoptotic bodies, and necrosis. D. The Ki-67 nuclear labeling index is >90% in small-cell carcinoma; 40x. E. Positive immunostaining for synaptophysin in small-cell carcinoma; 40x. F. Urothelial carcinoma invading thick bundles of smooth muscle diagnostic of detrusor-muscle invasion at transurethral resection.