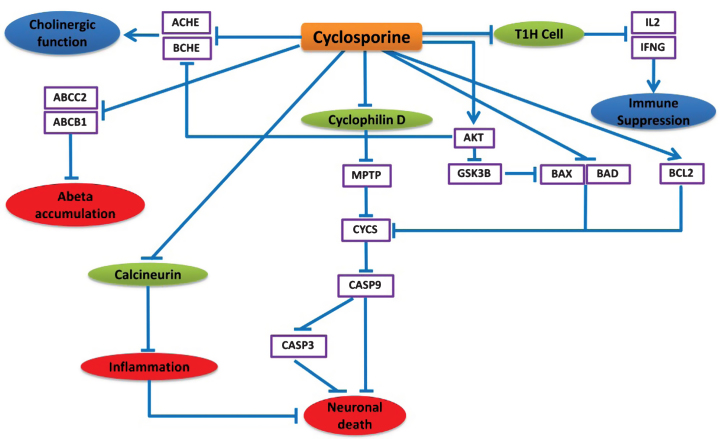
Fig.5.
Neuroprotective effects of cyclosporine in the context of AD. This cartoon demonstrates the mode of action of cyclosporine explicitly. The blue lines here represent the alternative effect of cyclosporine on these different pathways. Cyclosporine mainly inhibits T helper cells to suppress the immune system. Cyclosporine found to affect neuronal cell death by inhibiting cyclophilin D that prevents the cytochrome C release and CASP9, CASP3 activation. Cyclosporine can also down regulate ACHE and BCHE which can provide improved cholinergic function. Moreover, cyclosporine might be useful to prevent amyloid beta accumulation by preventing ABCC2 and ABCB1 proteins.