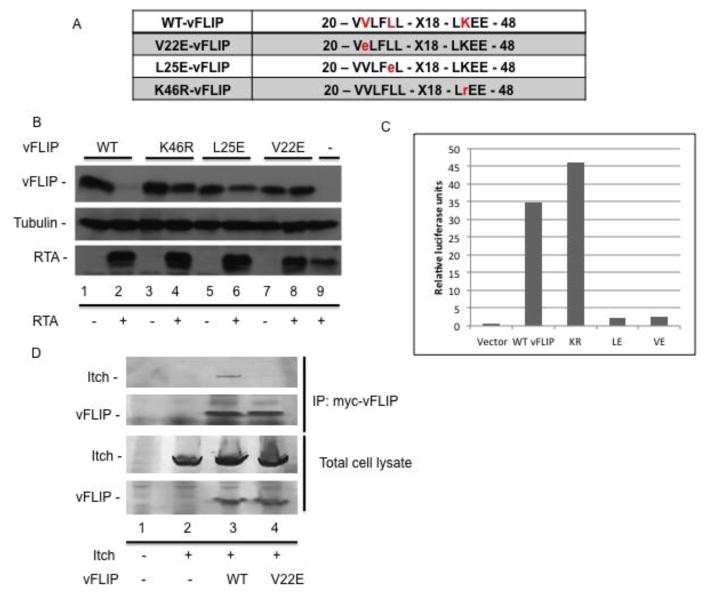
Figure 5.
Valine 22 is required for vFLIP interaction with Itch and sensitivity to degradation in the presence of RTA. A. Illustration of RTA resistant mutants of vFLIP. B. Mutations of amino acids 22, 25, and 46 in vFLIP confer resistance to RTA induced degradation. 293T cells were transfected with RTA and wild type or mutant vFLIP where indicated. 48h post transfection, cells were harvested and lysates were analyzed via immunoblot against myc-vFLIP, RTA, and tubulin. C. vFLIP V22E and L25E are unable to activate NFκB. NFκB activation was quantified using the Dual Luciferase reporter assay system. 293T cells were transfected with wild type or mutant vFLIP plus the two reporter plasmids pNFκB-Luc and pGL4.70 Renilla luciferase. Luciferase was measured and data were taken as a ratio of firefly/renilla luciferase. D. Valine 22 in vFLIP is required for vFLIP interaction with RTA. 293T cells were transfected with Flag tagged Itch and wild type or mutant vFLIP where indicated. 48h post transfection, cells were harvested and processed for immunoprecipitation. Precleared lysates were incubated with antibodies against myc-vFLIP followed by addition of protein A/G agarose and washed with RIPA buffer. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot using antibodies against myc-vFLIP and Flag-Itch.