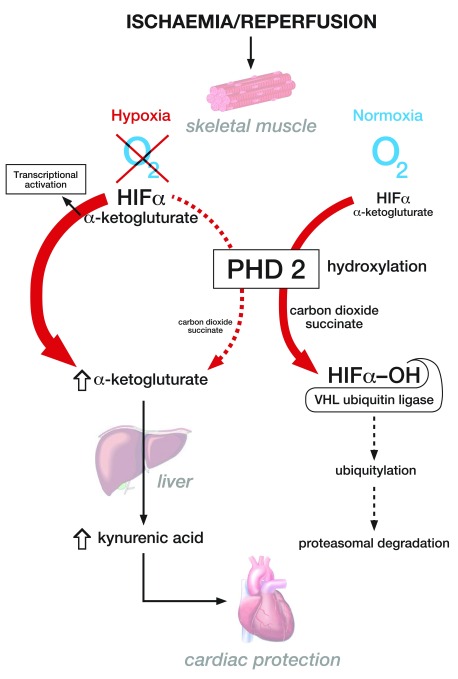
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the pathways involved in enhanced kynurenic acid (KYNA) generation by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) hydroxylase PHD2 during hypoxia.
The figure demonstrates the mechanism by which muscle hypoxia results in the inhibition of PHD2 function leading to enhanced alpha-ketoglutarate generation and kynurenic acid production, which may mediate a cardioprotective effect. It also shows the canonical role of PHD2 in normoxia in the oxygen-dependent degradation of the transcription factor HIF. HIFα, hypoxia inducible factor α; PHD2, prolyl hydroxylase domain 2; VHL, von Hippel Lindau.