Figure 3.
Quantities and Integrity of psaA-psaB Transcripts and Protein Labeling Studies.
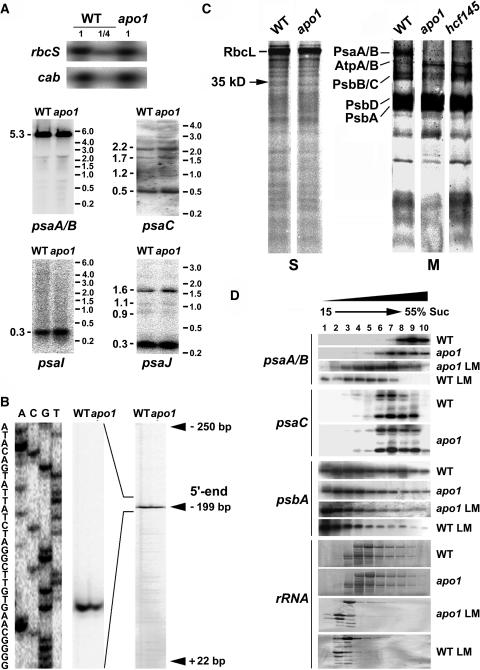
(A) RNA gel blot analysis of the plastid PSI genes and the nuclear cab and rbcS genes. Eight and two (1/4) μg of total RNA from three-week-old mutant and wild-type leaves were analyzed using gene-specific probes. Sizes of the standard (right) and the bands (left) are indicated in kilobases.
(B) Primer extension analysis of mutant and wild-type mRNA shows that the transcript 5′ termini at position −199 nt relative to the start codon of the psaA message are intact in apo1.
(C) In vivo labeling of plastid soluble (S) and membrane (M) proteins separated by SDS-PAGE in apo1, hcf145, and the wild type (WT). Wild-type and mutant proteins with equivalent amounts of radioactivity (100.000 cpm) were loaded.
(D) Polysome sedimentation in 15% to 55% sucrose (Suc) gradients by ultracentrifugation and subsequent RNA gel blot analysis of fractionated samples. Probes used are indicated at left. The filter used for the psaC probe was rehybridized with the psaA-psaB probe. The filter of the lincomycin-treated (LM) material was used for psaA-psaB and rehybridized with the psbA probe. Lincomycin treatment of wild-type and mutant plants was performed 4 h before polysome preparation. rRNAs have been detected by staining the blots.