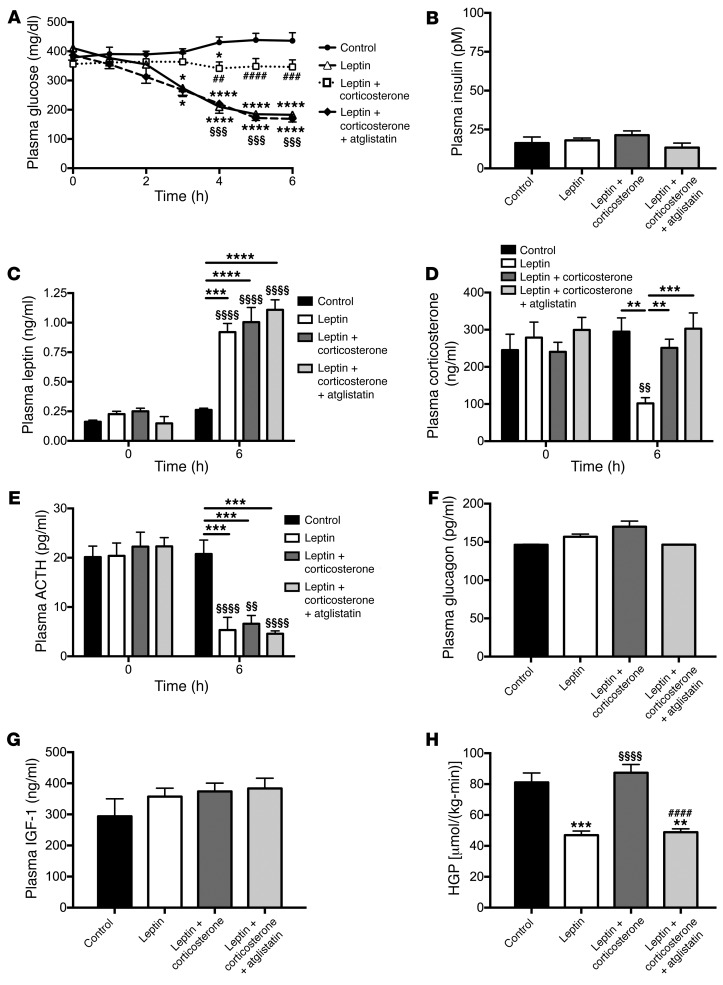
Figure 1. Leptin suppression of hypercorticosteronemia is required to mediate its glucose-lowering effects by suppressing lipolysis in DKA.
(A) Plasma glucose during a 6-hour acute infusion of saline (control), leptin, or leptin and corticosterone with or without pretreatment with atglistatin. (A and H) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 vs. controls; §§§P < 0.001, §§§§P < 0.0001 vs. leptin-treated rats; and ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, ####P < 0.0001 vs. leptin plus corticosterone–treated rats. (B) Fasting plasma insulin. (C–E) Plasma leptin, corticosterone, and ACTH concentrations at 0 and 6 hours of the infusion. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 between the groups indicated; §§P < 0.01, §§§§P < 0.0001 vs. the same group at time zero. (F and G) Fasting plasma glucagon and IGF-1 concentrations. (H) HGP after 6 hours. In all panels, data were compared by 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test, with data presented as the mean ± SEM of n = 7 (control), n = 7 (leptin), n = 10 (leptin plus corticosterone), and n = 6 (leptin plus corticosterone plus atglistatin) rats.