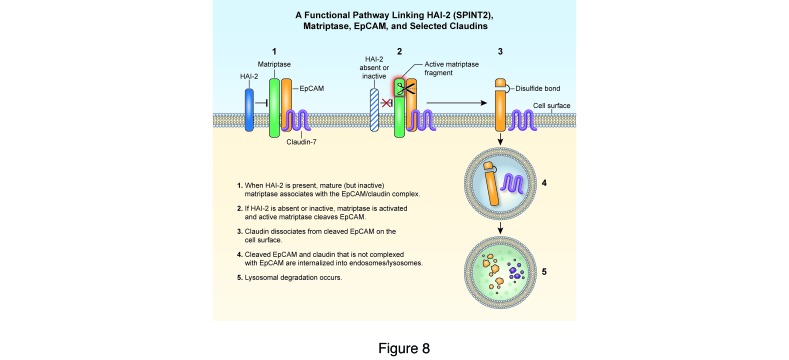
Figure 8. A functional pathway linking HAI-2/SPINT2, matriptase, EpCAM, and claudin-7.
EpCAM complexes with claudin-7 and colocalizes with matriptase on the lateral surfaces of polarized IECs. CTE-associated mutations in SPINT2 inactivate the matriptase inhibitor HAI-2. Unrestrained active matriptase then cleaves EpCAM, leading to dissociation of EpCAM and claudin-7 followed by internalization and lysosomal degradation of both EpCAM and claudin-7. The existence of this pathway explains why mutations in SPINT2, EPCAM, and CLD7 can cause very similar phenotypes.