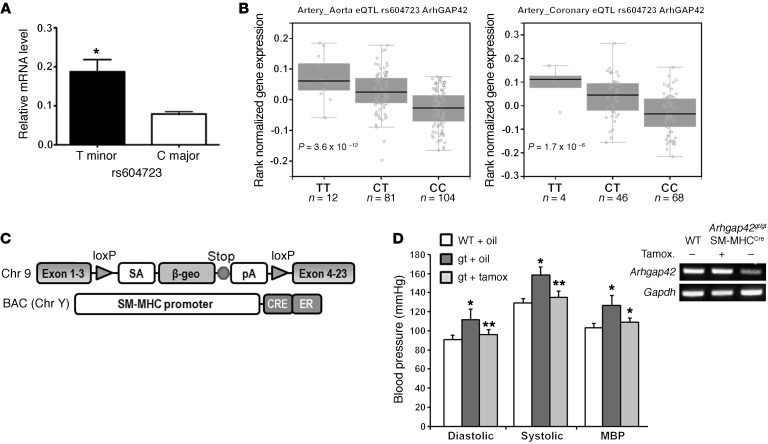
Figure 1. ARHGAP42 expression in SMCs is regulated by allele-specific mechanisms and controls BP.
(A) Total RNA isolated from HuAoSMCs heterozygous at the rs604723 SNP (C/T) was subjected to first-strand cDNA synthesis using reverse transcriptase. Reaction products were then subjected to a TaqMan-based PCR assay using allele-specific primers to the ARHGAP42 rs604723 variation. Data represent mean ± SEM of n = 4 experiments; *P < 0.01 vs. the major C allele (Student’s t test). (B) ARHGAP42 mRNA levels were measured by the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Consortium. The minor T ARHGAP42 allele at the rs604723 polymorphism was significantly associated with increased ARHGAP42 expression in aortic and coronary artery samples. (C) Schematic of the Arhgap42 gene-trap and SM-MHCCreERT2 mice used for SMC-specific ARHGAP42 rescue experiments. (D) WT and Arhgap42gt/gt SM-MHCCreERT2 mice were injected i.p. with vehicle (corn oil) or tamoxifen (100 mg/kg) for 5 consecutive days as indicated. Two weeks after the last injection, BP was measured by tail cuff method, and Arhgap42 mRNA levels in the aorta were measured by semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis using primers to exons 1 and 4. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 6 for WT and Arhgap42gt/gt SM-MHCCreERT2 mice with vehicle treatment, n = 5 for Arhgap42gt/gt SM-MHCCreERT2 mice with tamoxifen treatment. *P < 0.05 vs. WT; **P < 0.05 vs. corn oil–treated (ANOVA). Note that tamoxifen treatment restored Arhgap42 expression and reduced BP to WT levels (representative of 3 separate experiments).