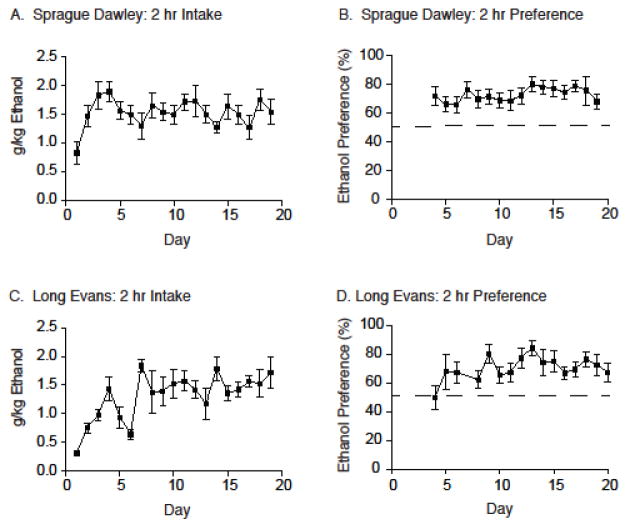
Figure 1.
The intermittent two-bottle choice paradigm was sufficient in establishing ethanol drinking and preference in both Sprague Dawley and Long Evans rats. (A) Total ethanol consumed (g/kg) is reported over the course of the 19-day acquisition period at the 2-hour time point for Sprague Dawley rats (N=19). (B) Ethanol preference (%) is reported over the course of the 19-day acquisition period at the 2-hour time point for Sprague Dawley rats (N=19). (C) Total ethanol consumed (g/kg) is reported over the course of the 19-day acquisition period at the 2-hour time point for Long Evans rats (N=6). (D) Ethanol preference (%) is reported over the course of the 19-day acquisition period at the 2-hour time point for Long Evans rats (N=6).