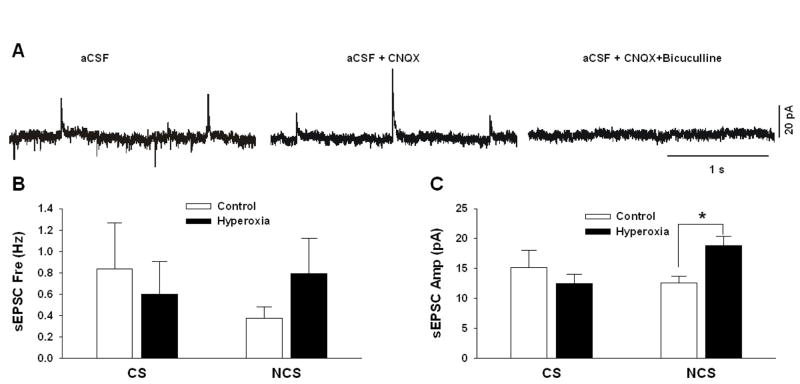
Fig. 6.
Representative traces of post-synaptic currents for a cNTS neuron from a neonatal rat reared in 21% O2 in aCSF (A: left panel), in aCSF plus the AMPA-receptor antagonist CNQX (A: middle panel) and in aCSF plus CNQX and the GABA-A-receptor antagonist bicuculline (A: right panel). Excitatory post-synaptic currents (EPSC) are shown by downward deflections of the current trace and inhibitory post-synaptic currents (IPSC) are shown by upward deflections of the current trace. The frequency (B) and amplitude (C) of spontaneous EPSCs (sEPSC) are shown for both chemosensitive (CS) and non-chemosensitive (NCS) cNTS neurons from Control rats (reared in 21% O2) and from Hyperoxia rats (reared in 60% O2). Values are mean±SEM. Number of observations (Control, Hyperoxia): CS (n=4, 5), NCS (n=6, 5). * P<0.05 vs. Control.