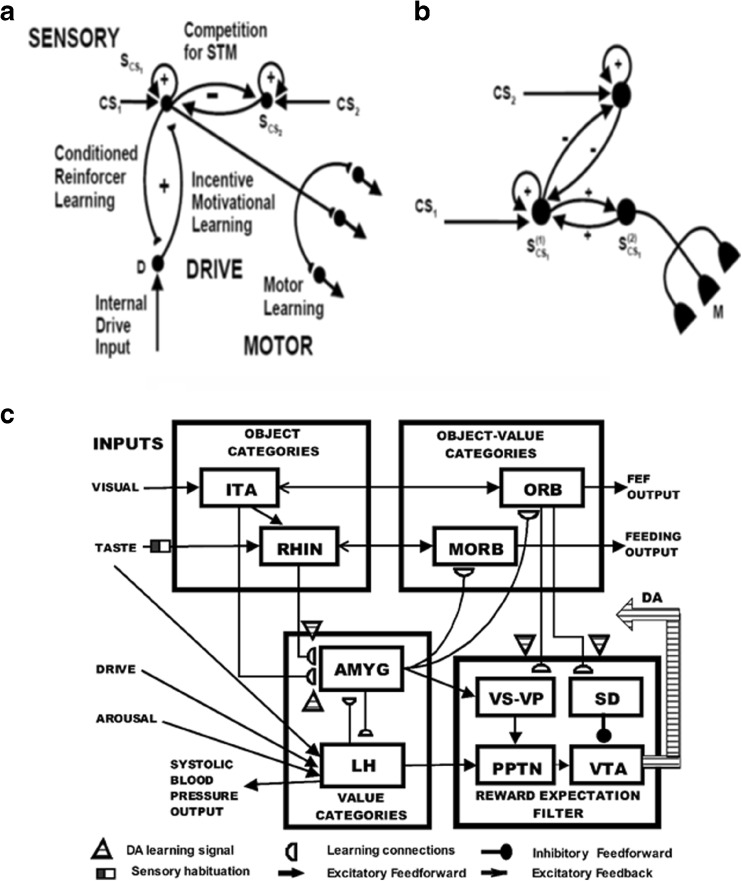
Fig. 4.
(a) The simplest Cognitive-Emotional-Motor (CogEM) model: Three types of interacting representations (sensory, S; drive, D; and motor, M) that control three types of learning (conditioned reinforcer, incentive motivational, and motor) help to explain many reinforcement learning data. (b) In order to work well, a sensory representation S must have (at least) two successive stages, S(1) and S(2), so that sensory events cannot release actions that are motivationally inappropriate. The two successive stages of a sensory representation S are interpreted to be in the appropriate sensory cortex (corresponds to S(1)) and the prefrontal cortex, notably the orbitofrontal cortex (corresponds to S(2)). The prefrontal stage requires motivational support from a drive representation D such as amygdala, to be fully effective, in the form of feedback from the incentive motivational learning pathway. Amydgala inputs to prefrontal cortex cause feedback from prefrontal cortex to sensory cortex that selectively amplifies and focuses attention upon motivationally relevant sensory events, and thereby “attentionally blocks” irrelevant cues. [Reprinted with permission from Grossberg and Seidman (2006).] (c) The amygdala and basal ganglia work together, embodying complementary functions, to provide motivational support, focus attention, and release contextually appropriate actions to achieve valued goals. For example, the basal ganglia substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) releases Now Print learning signals in response to unexpected rewards or punishments, whereas the amygdala generates incentive motivational signals that support the attainment of expected valued goal objects. The MOTIVATOR model circuit diagram shows cognitive-emotional interactions between higher-order sensory cortices and an evaluative neuraxis composed of the hypothalamus, amygdala, basal ganglia, and orbitofrontal cortex [Reprinted with permission from Dranias et al. (2008)]