Fig. 1.
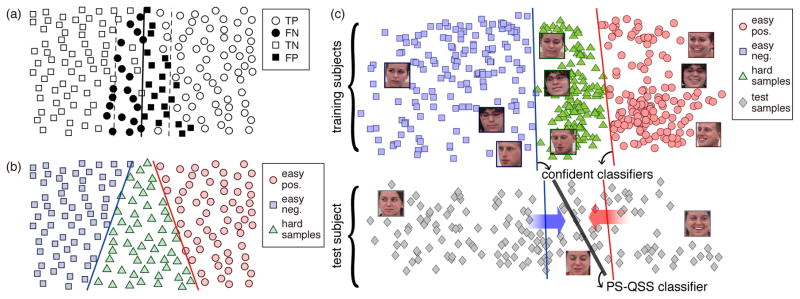
The main idea of Confidence Preserving Machine (CPM): (a) A standard single-margin classifier identifies true positive (TP), true negative (TN), false positive (FP) and false negative (FN). Data within the margin (dashed lines) consist of mostly FP and FN, producing undesired ambiguities for training a classifier. (b) The proposed confident classifiers, two hyperplanes that are not necessarily parallel, reveal easy and hard samples for preserving confident predictions in each class. (c) The proposed CPM, consisting of confident classifiers and a person-specific (PS) classifier using a quasi-semi-supervised (QSS) learning strategy, is trained to propagate predictions from confident test samples (easy test samples) to hard ones.