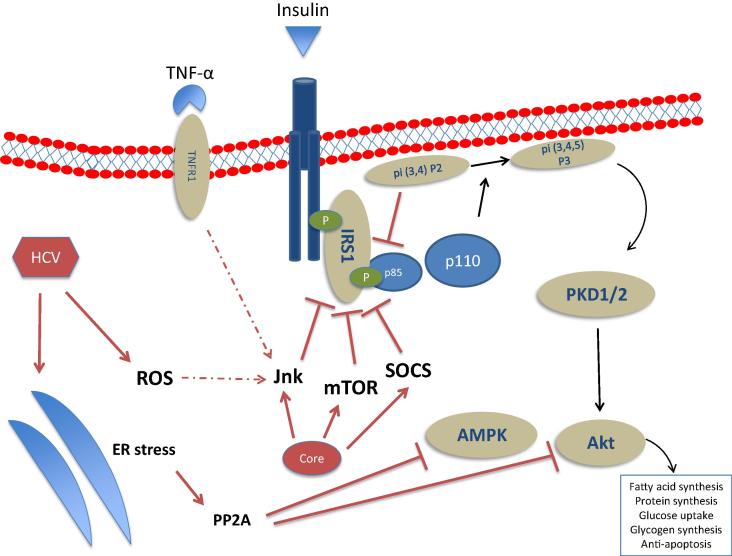
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the HCV interactions (both direct and indirect) on the hepatocyte insulin signaling pathway. HCV core can directly activate inhibitors of insulin signaling: the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), the suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-3, and the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). HCV increases endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress which can lead to the activation of the protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), an inhibitor of Akt and AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) which are key regulators of gluconeogenesis. Other abbreviations: PKD1/2: protein kinase D1/2; p85/p110: subunits p85 and p110 of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.