Fig. 2.
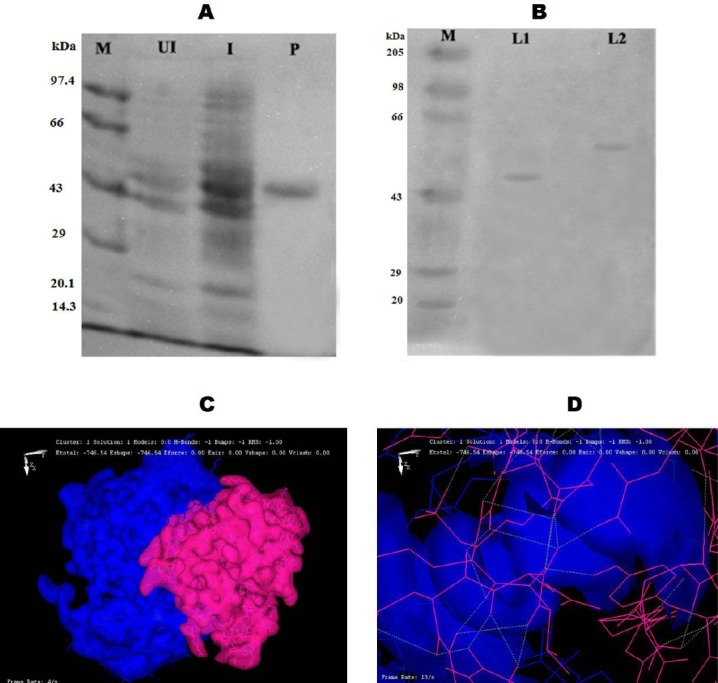
Structural and functional analysis of phosphorylated glkA. A) The expression and purification of rglkA from glkA1 clone using SDS-PAGE (10%). Lane M, protein molecular weight markers (Merck Bioscience, India Pvt. Ltd.); Lane UI, uninduced cytosolic fraction of glkA1 clone.; lane I, isopropyl-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside-induced cytosolic fraction of glkA1 clone; Lane P, nickel metal agarose column purified glkA. B) SDS-PAGE (10%) gel showing phosphorylated rglkA identified by reagent A, followed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining. Lane M, protein molecular weight markers (Merck Bioscience, India Pvt. Ltd.); lane L1, normal rglkA; lane L2, phosphorylated rglkA. C) An image showing the formation of hydrogen bond between the glkA protein (blue) and BYK protein (pink). D) An image showing the interaction of ATP-binding site of glkA protein (blue) with BYK protein (pink).
