Fig. 3.
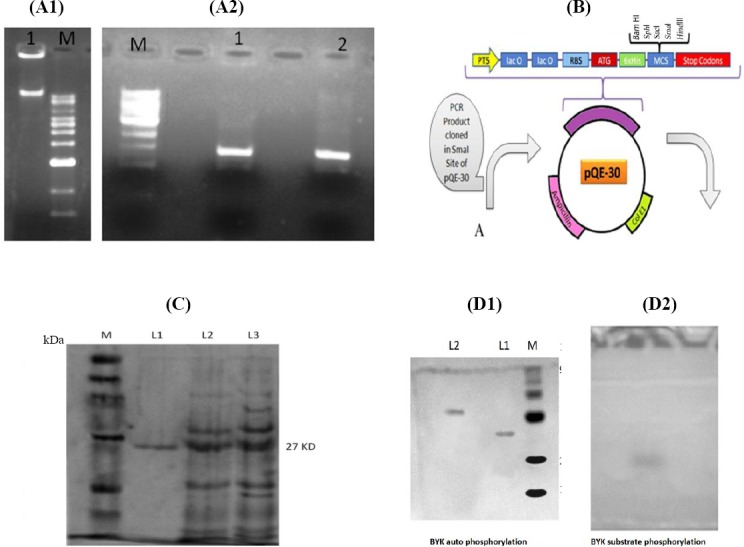
Cloning, expression, and characterization of BYK. A1) 1% agarose gel showing the presence of chromosomal DNA from S. aureus ATCC 12600. Lane 1, chromosomal DNA of S. aureus ATCC 12600; Lane M, molecular size marker. A2) PCR amplification of BYK gene of S. aureus ATCC 12600. Lane M, molecular size marker (33,500-500 bp); Lanes 1 and 2, PCR-amplified products. B) The schematic representation of pQE-30 plasmid vector. A represents PCR product cloned in the SmaI site of pQE vector. C) Expression and purification of rBYK from BYK-1 clone using SDS-PAGE (10%). Lane M, protein molecular weight markers (Merck Bioscience Private Ltd., India); Lane L1, nickel metal agarose column purified BYK; Lane L2, cytosolic fraction of uninduced BYK-1 clone; Lane L3, cytosolic fraction of isopropyl-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside-induced BYK-1 clone. D1) SDS-PAGE gel showing phosphorylated rBYK identified by reagent A, followed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining. Lane M, protein molecular weight marker; Lane L1, normal rBYK; Lane 2, phosphorylated rBYK. D2) Pure phosphorylated rBYK and substrate BYKs separated in SDS-PAGE. All markers were obtained from Bangalore Genei Private Ltd. (India) otherwise stated.
