Figure 3.
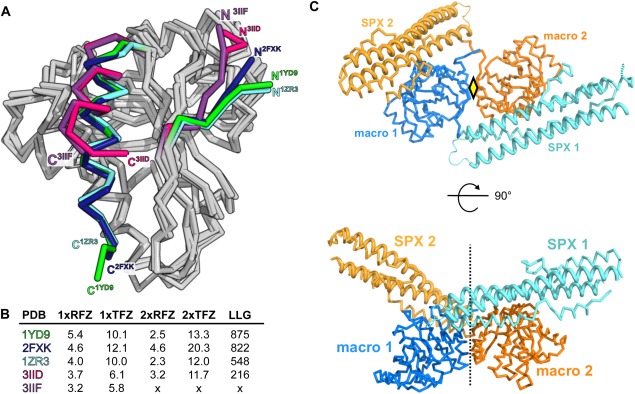
The known macro domain structures allow for structure solution of SPXScVtc 4 by molecular replacement. (A) Structural superposition of different, previously described macro H2A1.1 macro domain structures indicates that N‐ and C‐termini are flexible. R.m.s.d. is between 0.7‐2.6 Å comparing 180 corresponding Cα atoms. (B) Table summary of molecular replacement calculations using the different known macroH2A1.1 structures. 1xRFZ: rotation function Z‐score for the 1st molecule to be placed. 1xTFZ: translation function Z‐score for the 1st molecule to be placed. 2xRFZ: rotation function Z‐score for the 2nd molecule to be placed. 2xTFZ: translation function Z‐score for the 2nd molecule. LLG: Log Likelihood Gain of the refined solution. (C) Cα traces of two SPXScVtc4‐macro molecules (SPX domain are shown in light‐blue and yellow, the C‐terminal macro domains in dark‐blue and orange, respectively) related by a pseudo 2‐fold axis in the asymmetric unit of the I212121 crystal form. The central core helices of the SPX domains are highlighted (ribbon diagrams).
