Figure 1.
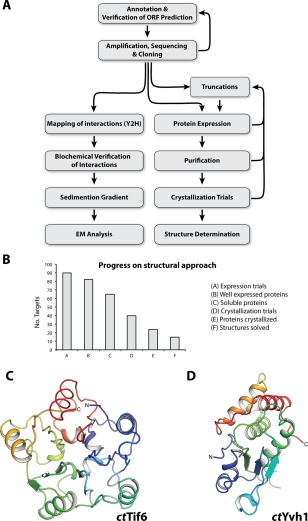
From gene identification to structure determination of ribosome biogenesis factors. (A) Scheme depicts the workflow from in silico ORF annotation to cloning, expression, determination of the interactome, biochemical characterization and structural analysis by cryo EM or crystallography. (B) Statistics of the structural approach. From 90 targets that were tested for expression in E. coli (column A), 77 were well expressed (column B) and 52 were soluble (column C), which went into large‐scale purification. Subsequently, 40 proteins were suitable for crystallization trials (column D), of which 24 yielded crystals (column E), and finally allowed determination of 14 structures (column F). (C,D) Crystal structure of the phosphatase domain (PD) of ctTif6 (C, pdb: 5M3Q) and ctYvh1 (D, pdb: 5M43) both colored from N‐ to C‐terminus (blue to red). The overall structure of ctTif6 is highly similar to that of scTif6 (RMSD 0.67 Å over 216 residues), with an internal fivefold symmetry. The phosphatase domain of ctYvh1 belongs to the family of dual‐specificity phosphatases, able to hydrolyze phosphate from phosphorylated serine/threonine as well as tyrosine residues.
