Figure 2.
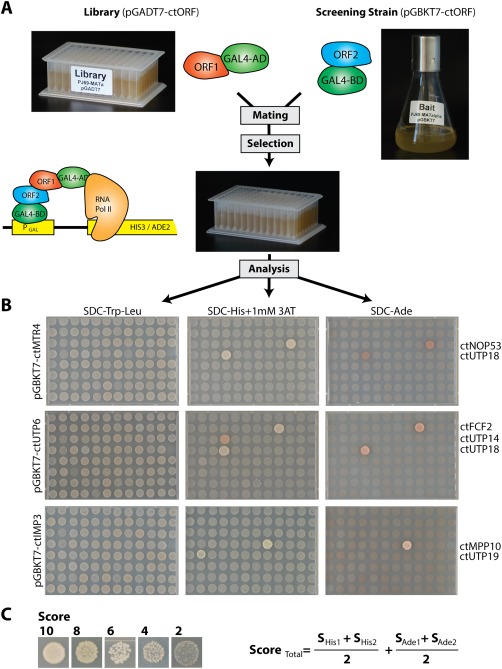
Illustration of the screening procedure for Y2H interactions. (A) Scheme of the experimental setup of the Y2H screen. Yeast strain PJ69‐4 MATa was transformed with 181 different Prey plasmids pGADT7 and a mix of five transformants was transferred to one position within two 96 deep well plates, representing the yeast‐two‐hybrid (Y2H) library. During the screening procedure, a liquid culture of the yeast strain (PJ69‐4 MATalpha) carrying the bait protein (pGBKT7) was mated against the refreshed library in a 96 deep well plate in liquid YPD medium. The next day, YPD was replaced with SDC‐Trp‐Leu medium to select for diploid cells carrying both plasmids. (B) After 2 day's incubation (30°C), the cells were spotted on SDC‐Trp‐Leu plates to control the mating efficiency, and on SDC‐Trp‐Leu‐His + 1 mM 3‐AT and SDC‐Trp‐Leu‐Ade plates to screen for medium and strong interactions. Plates were incubated at 30°C and documented after four and 7 days. Examples are shown in B. Bait proteins are listed on the left side and interacting prey proteins are indicated at the right side. (C) The strength of the Y2H interaction was ranked based on size and numbers of colonies. The total score was calculated from the mean value of 2 repetitions and the sum of the score derived from growth on SDC‐Trp‐Leu‐His11 mM 3‐AT and SDC‐Trp‐Leu‐Ade plates. The detected interactions are summarized in Supporting Information Tables S3 and S4 and can be viewed together with the primary data at http://y2h.embl.de.
