Figure 1. Venn diagram of genomic loci associated with HbA1c, fasting glucose, fasting proinsiulin, 2-hour glucose, and type 2 diabetes detected by GWAS.
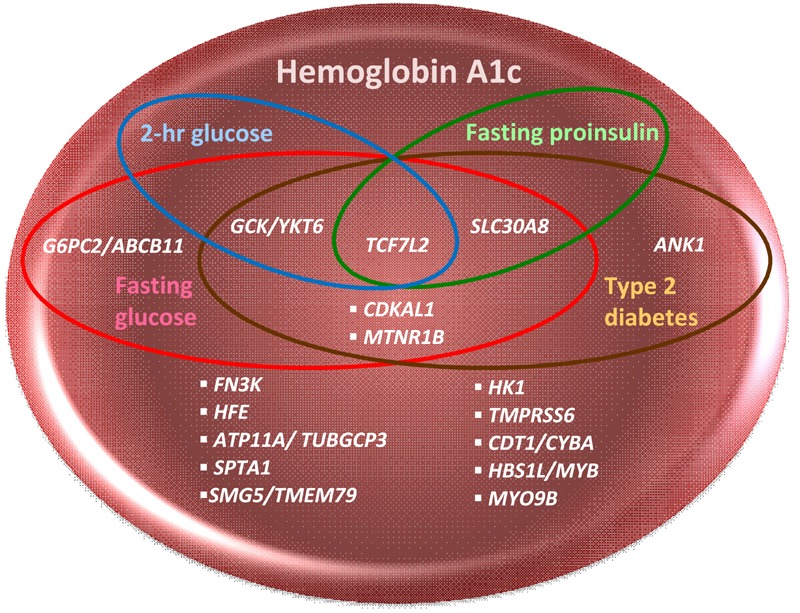
This Venn diagram depicts overlapping sets of HbA1c-related genomic loci which are also associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D, Mahajan et al. 2014, DIAbetes Genetics Replication and Meta-analysis (DIAGRAM) consortium), fasting glucose (FG), fasting insulin (FI), 2-hour glucose (2hrG, Scott et al., 2012, Meta-Analysis of Glucose and Insulin related traits Consortium (MAGIC)), and fasting proinsulin (PI, Strawbridge et al., 2011, MAGIC) in GWAS [21-23]. PI, a precursor of insulin in secretory granules of the pancreatic beta-cell, has minimal insulin activity until it has been processed to insulin. Elevated circulating levels of PI are associated with impaired beta-cell function, decreased insulin processing or secretion, or "beta-cell stress" resulting from insulin resistance [87]. PI, similarly to HbA1c, FG, 2hrG, and FI, is a predictor of future T2D [88]. Six HbA1c GWAS loci are glycemic: one (G6PC2/ABCB11) is associated with FG only, and five are associated with both T2D and FG GWAS loci, with three of these five (TCF7L2, GCK/YKT6, and SCL30A8) also associating with either 2hrG or PI. The HbA1c index SNP in ANK1 was considered "nonglycemic" when it was first discovered, although a T2D index SNP within ANK1 has been found in later GWAS. None of the HbA1c GWAS loci overlap with FI.
