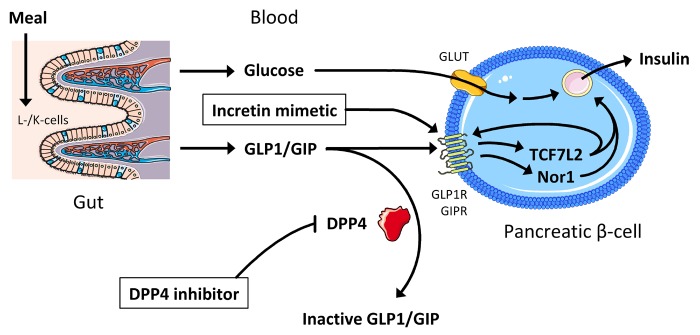
Figure 3. Pathways contributing to the pharmacodynamics of incretin mimetics and DPP4 inhibitors.
Incretins are released by specialized cells in the intestine (GLP1 by L-cells, GIP by K-cells). They enhance glucose-stimulated insulin secretion via binding to transmembrane receptors in pancreatic β-cells and, at least in part, subsequent activation of transcription factors, such as TCF7L2 and Nor1. Incretins are inactivated by DPP4 which is the target of DPP4 inhibitors. Incretin mimetics are stable incretin analogues bypassing DPP4. Abbreviations: DPP4 – dipeptidyl peptidase 4; GIP(R) – gastric inhibitory peptide (receptor); GLP1(R) – glucagon-like peptide 1 (receptor); GLUT – glucose transporter; Nor1 – neuron-derived orphan receptor 1; TCF7L2 – T-cell-specific transcription factor 7-like 2.