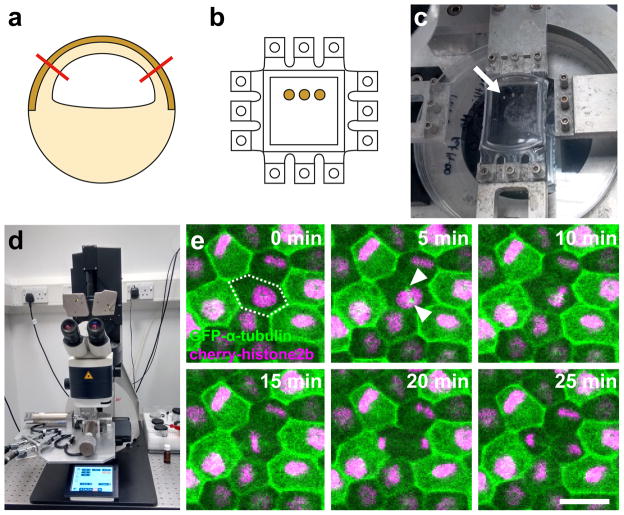
Figure 1. Method to simultaneously apply a reproducible strain and analyse cell division in the Xenopus animal cap.
a) The animal cap is dissected (red lines) from an early gastrula stage embryo that has been labeled by injection of GFP-α-tubulin and Cherry-histone2B mRNAs at the 2 cell stage. The dark brown area indicates the pigmented apical cell layer that will be imaged. b) Animal caps are cultured on a fibronectin coated flexible PDMS membrane until adhered. The PDMS membrane is cast in a custom mould with teeth on all four sides allowing either a uni-axial or biaxial stretch to be applied. c) PDMS membrane with cultured animal caps (arrow) attached to stretch apparatus. A uniaxial stretch is applied to stretch the animal caps by 35%; the teeth orthogonal to the stretch direction have been removed. d) The stretch apparatus is attached to the stage of an upright confocal microscope; a water-dipping objective is used to visualize cells in the apical layer. e) Example timelapse series using maximum intensity projections of cell division in the apical cell layer with frames 5 minutes apart. 35% stretch was applied in horizontal direction. The dividing cell is marked by dashed outline at 0 min, GFP-α-tubulin (green) labels the microtubule cytoskeleton and condensing centrosomes (arrowheads), Cherry-histone2B (magenta) labels nuclei. Scale bar: 30μm.