Table 1.
Overview of biomechanical methods used in Xenopus embryos
| Method and reference | Schematic | Overview | Mechanical property measured | Tissue studied | Quantitative? | Destructive? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue dissection (Beloussov et al., 1975) |

|
Tissue cut with blade and immediate deformation observed | Map location and direction of mechanical stresses in embryo | Whole embryo | No | Yes |
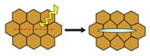
| Laser Ablation (Hara et al., 2013) |
|
Wound tissue with laser and record recoil velocity | Map location and direction of mechanical stresses in embryo | Whole embryo or expant | No | Yes |
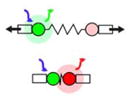
| Strain mapping (Kim et al., 2014; Feroze et al., 2015; Yamashita et al., 2016) |
|
Observation of movement and deformation of cells in tissue allows forces to be inferred | Map location and direction of mechanical stresses in embryo and/or estimate the distance a mechanical signal propogates | Whole embryo or expant | No | No |
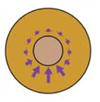
| FRET-based tension sensor (Yamashita et al., 2016) |
|
Measure FRET around an elastic linker within protein that can experience tension. | Tension at the molecular level | Whole embryo | No | No |
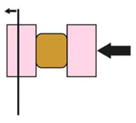
| nNewton Force Measurement (Moore et al., 1995; Davidson and Keller, 2007) |
|
Tissue explant uniaxially compressed against a cantilever | Viscoelastic properties of explant | Brick shaped explant | Yes | Explant cut |
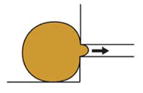
| Microaspiration (von Dassow et al., 2010) |
|
Measure length of tissue drawn into a channel of known diameter under negative pressure | Viscoelastic properties of embryo | Whole embryo | Yes | No |
| Axisymmetric drop shape analysis (Kalantarian et al., 2009; Luu et al., 2011; David et al., 2014) |
|
Measure deformation of an explant or cellular aggregate over time | Surface tension of the explant or aggregate | Explant or cellular aggregate | Yes | Yes |
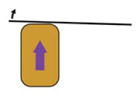
| Cantilever based measurement of migration force (Hara et al., 2013) |
|
A migrating explant pushes against a cantilever | Force produced during explant migration | Leading edge mesoderm explant | Yes | Explant cut |
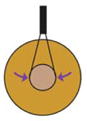
| Insertion of cantilevers into embryo (Feroze et al., 2015) |
|
Morphogenetic movements of blastopore closure push directly on inserted cantilever | Force produced during blastopore closure | Whole embryo | Yes | No |
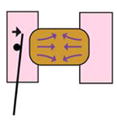
| Tractor pull assay (Pfister et al., 2016) |
|
Covergence and extension of explant pulls on sled and moves cantilever | Force produced during convergence and extension | Giant explant | Yes | Explant cut |
| 3D Force Microscopy (Zhou et al., 2015) |
|
Force produced by explant embedded in gel measured by fluorescent bead displacement. | Force produced during morphogenetic movements | Dorsal explant | Yes | Explant cut |
