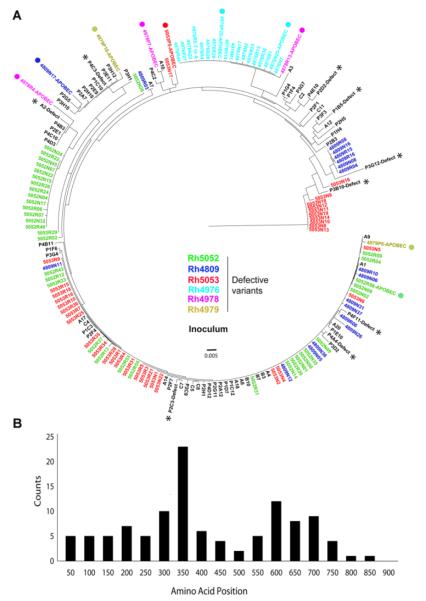
Fig 5. Defective post-transmission variants were primarily caused by frameshift.
(A) The phylogenetic relationship of defective post-transmission variants with all the variants in the inoculum. Defective post-transmission variants are color coded by animal ID and are phylogenetically associated with inoculum functional rather than defective variants. The majority of post-transmission defective variants are caused by frameshift. The APOBEC mediated mutations are labeled with solid circles. All variants in the inoculum are shown in black with defective variants labeled with stars. (B) The distribution of the first introduced stop codon in post-transmission defective variants. The peak of the first stop codon location is near the V3 region and very few are located within the cytoplasmic tail of GP41.