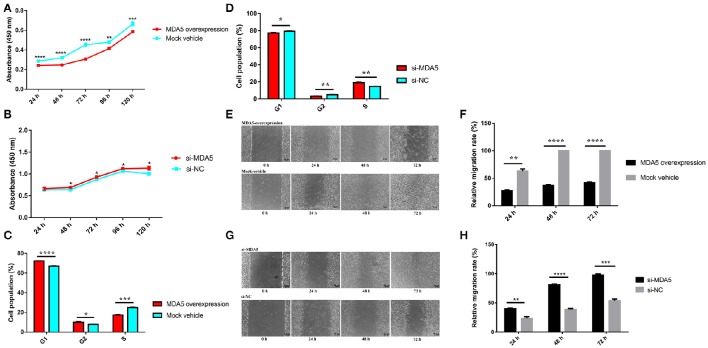
Figure 4.
MDA5 mediates the effects of miR-34b-5p on the proliferation, cell cycle, and migration of ALV-J-infected DF-1 cells. (A) Cell growth was significantly reduced after the transfection of an MDA5 overexpression plasmid compared to control cells (n = 6). (B) Cell growth was significantly increased after the transfection of a siRNA targeted against the MDA5 gene compared to control cells (n = 6). (C) Overexpression of MDA5 resulted in increased proportions of cells in the G1 and G2 phases and a decreased proportion of cells in the S phase. (D) Knockdown of MDA5 resulted in an increased proportion of cells in the S phase and decreased proportions of cells in the G1 and G2 phases. (E) Representative images of the wound healing assay at 0, 24, 48, and 72 h after the ALV-J infections with MDA5 overexpression in DF-1 cells. (F) Quantification of the wound healing assay of MDA5 overexpression at 24, 48, and 72 h after the ALV-J infections. (G) Representative images of the wound healing assay at 0, 24, 48, and 72 h after the ALV-J infections in MDA5 knockdown DF-1 cells. (H) Quantification of the wound healing assay in MDA5 knockdown DF-1 cells. In panels (A,B), the results were confirmed by three independent experiments with six (cell number) samples per treatment. In panels (C,D,F,H), the data shown are the mean ± the SEM from three independent experiments. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences: *, **, ***, and **** indicate P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P < 0.001, and P < 0.0001, respectively. ALV-J, Avian leukosis virus subgroup J; MDA5, melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5; SEM, standard error of the mean; siRNA, small interfering RNA.