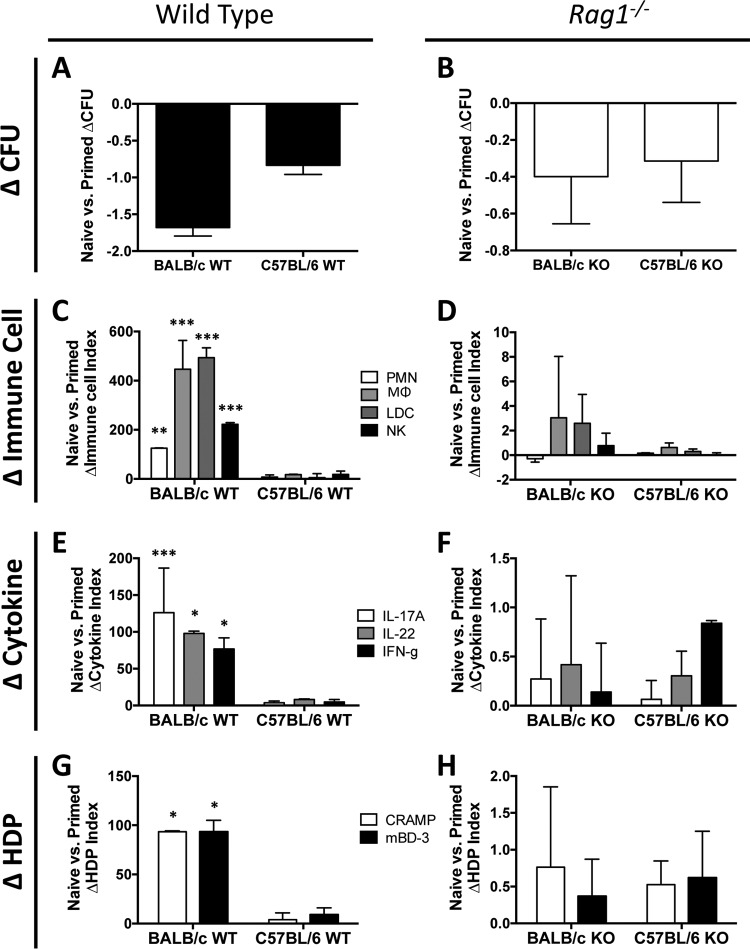
FIG 9.
Priming in different mouse genetic backgrounds yields differential proinflammatory responses. Differences in MRSA burdens and proinflammatory responses in the skin are shown for naive versus primed mice. Differences in mean log10 CFU between primed and naive mice were calculated for the wild-type (A) and rag1−/− (B) genotypes for both the BALB/c and C57BL/6 mouse backgrounds. The changes in indices of immune cell infiltration (C and D), cytokine expression (E and F), and host defense peptide (HDP) induction (G and H) between naive and primed mice were calculated for the wild-type (C, E, and G) and rag1−/− (D, F, and H) genotypes for both the BALB/c and C57BL/6 backgrounds. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (versus C57BL/6 mice via Student's t test). Data presented are means and SD for index differences between the naive and primed groups.