FIG 5.
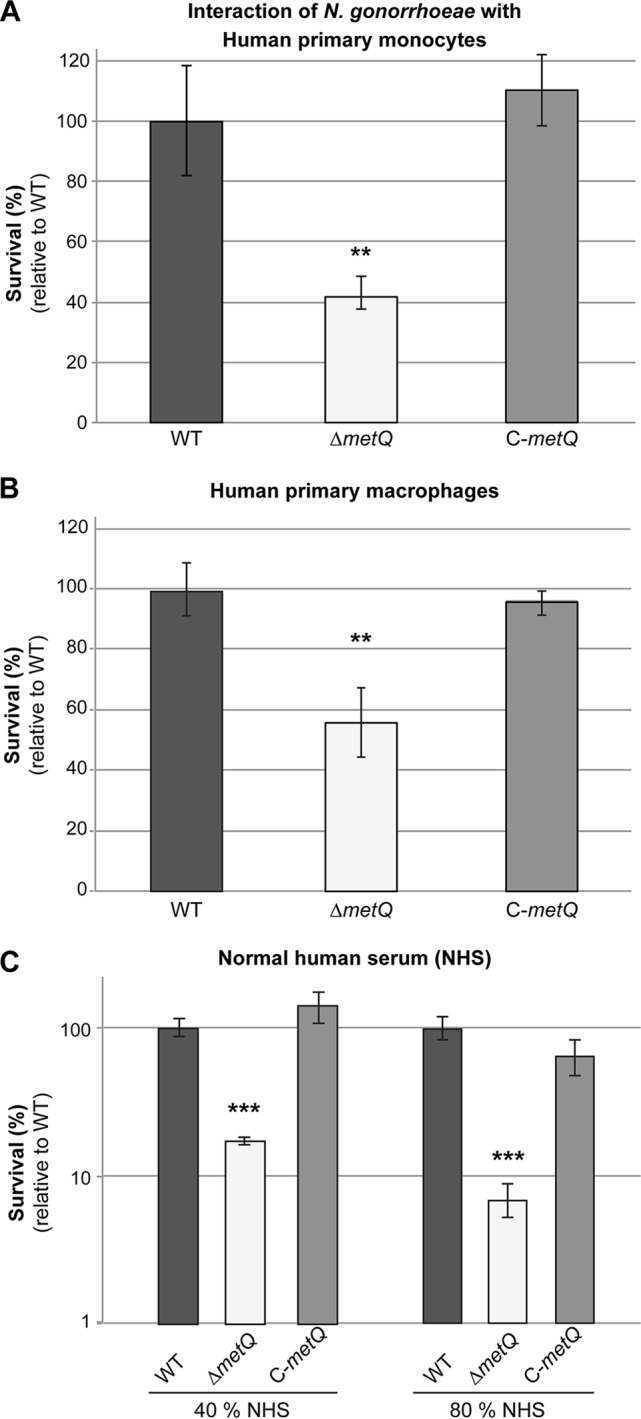
Role of MetQ in survival in monocytes, macrophages, and human serum. Survival of the N. gonorrhoeae 1291 wild-type (WT), metQ knockout (ΔmetQ), and complemented (C-metQ) strains with primary monocytes (A), activated macrophages (B), and normal human serum (NHS) (C). Data represent the average percent survival for triplicate samples as a percentage of the inoculum size and are shown relative to the results obtained with the wild-type strain (the results for the wild type, set at 100%, are 2.4 × 104 CFU for monocytes, 1.2 × 105 CFU for macrophages, 7.0 × 104 CFU for 40% normal human serum, and 1.9 × 104 CFU for 80% normal human serum). Error bars represent ±1 standard deviation. **, P ≤ 0.01 for the ΔmetQ strain relative to the wild type, using a two-tailed Student's t test; ***, P ≤ 0.001 for the ΔmetQ strain relative to the wild type, using a two-tailed Student's t test. Experiments were performed on at least three occasions, and representative results are shown.
