FIG 6.
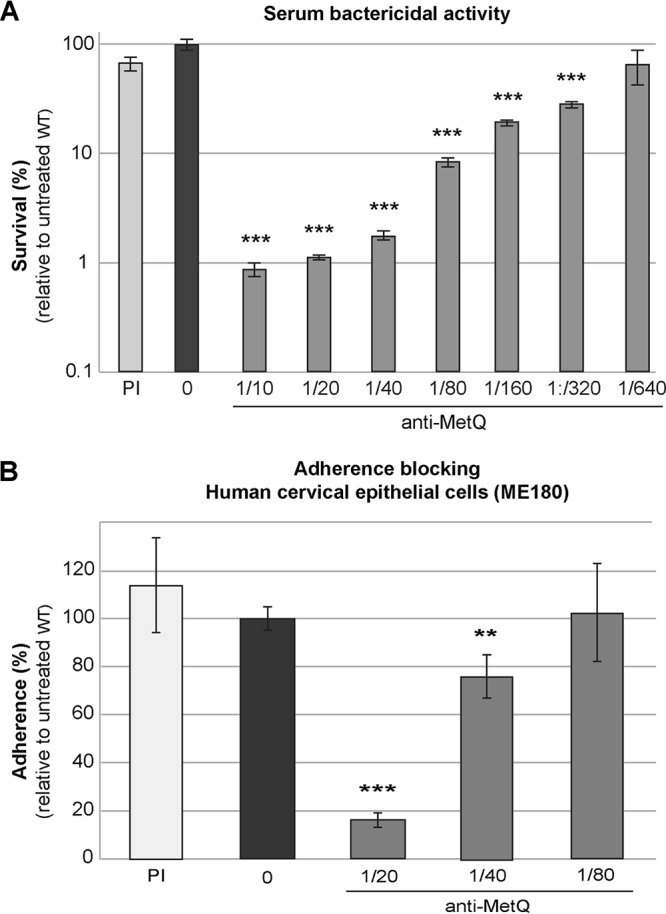
Functional activity of anti-MetQ antibodies. (A) Serum bactericidal activity. The survival of the wild-type (WT) strain in the presence of a 1/10 dilution of preimmune serum (PI) or 2-fold dilutions of heat-inactivated anti-MetQ mouse polyclonal serum with 10% normal human serum (preabsorbed with N. gonorrhoeae) as a source of complement is shown. (B) Blocking of adherence to cervical epithelial cells. The adherence of the wild-type strain in the presence of a 1/20 dilution of preimmune serum or 2-fold dilutions of heat-inactivated anti-MetQ mouse polyclonal sera is shown. Data represent the average survival (A) or adherence (B) for triplicate samples as a percentage of the inoculum size and the adherence of the inoculum and are shown relative to the result obtained with the untreated wild-type strain (the results for the untreated wild type, set at 100%, are 1.8 × 105 CFU for serum bactericidal activity and 9.1 × 104 CFU for adherence). Error bars represent ±1 standard deviation. In both panels A and B, there was a statistically significant difference between groups, as determined by one-way ANOVA [F(9, 20) = 46.58 and P = 1.8 × 10−11 and F(6, 21) = 32.5 and P = 1.4 × 10−9, respectively]. **, P ≤ 0.01 relative to the untreated wild type, using a two-tailed Student's t test; ***, P ≤ 0.001, relative to the untreated wild type, using a two-tailed Student's t test. Experiments were performed on at least three occasions, and representative results are shown.
