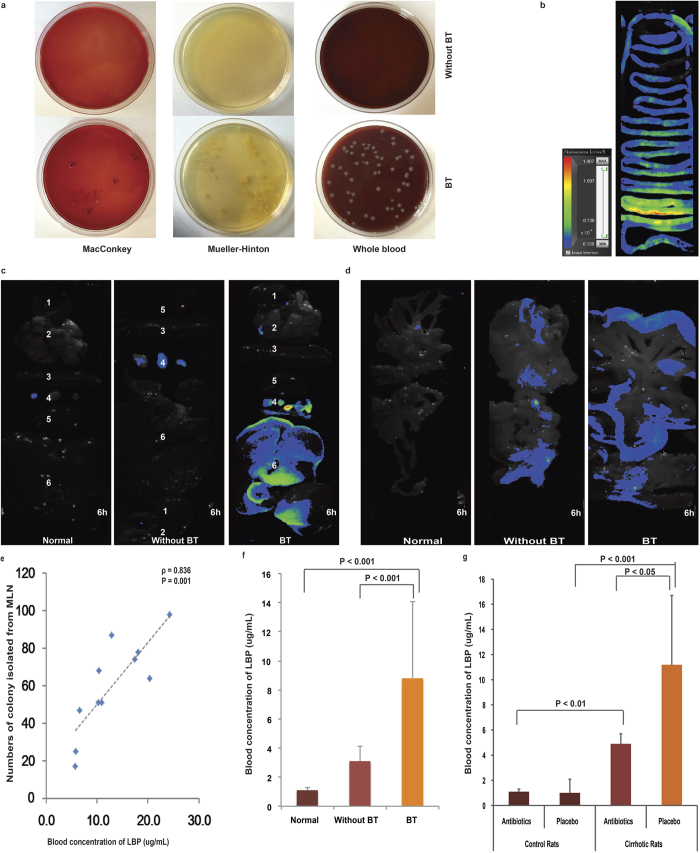
Figure 1. CCl4-induced cirrhosis increases the incidence of BT in rats.
(a) Results of representative culture experiments using MLNs in cirrhotic rats with or without BT. (b) Correlations between the numbers of colonies isolated from the MLNs and plasma LBP levels were determined using Spearman’s rank test. (c) Plasma LBP concentrations in cirrhotic rats with and without BT and normal rats. (d) Plasma LBP concentration in antibiotic- or placebo-treated cirrhotic rats and normal rats. (e–g) A separate experiment was performed in which cirrhotic rats with ascites were administered 108 RFP-tagged E. coli via gavage. Six hours later, RFP-marked E. coli were observed along the intestinal tract (e), in MLNs and the liver (f), and in the mesentery (g).