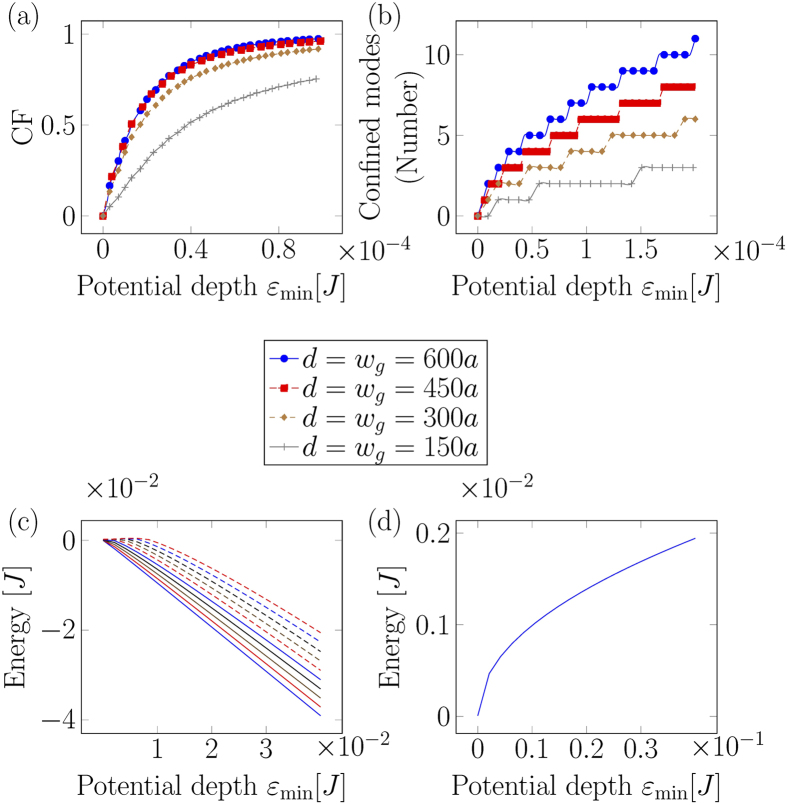
Figure 4.
(a) Confinement factor as a function of εmin[J] for several values of d. To achieve the same CF, a potential with smaller d requires larger εmin[J]. (b) Number of confined modes inside the potential. The criterion of confinement was chosen to be the value of CF. When CF of a particular mode reaches 0.9, we considered it a confined mode. A similar dependence on d holds true here, where smaller d needs a stronger potential to confine the same number of modes as a guide with larger d. (c) Ten lowest eigenvalues as a function of εmin[J], d = wg = 150a. A value below zero is a bound mode. As the potential depth increases, more and more modes become bound modes. (d) The difference between ground state and the first excited state. The difference also increases with the increasing depth of the potential.