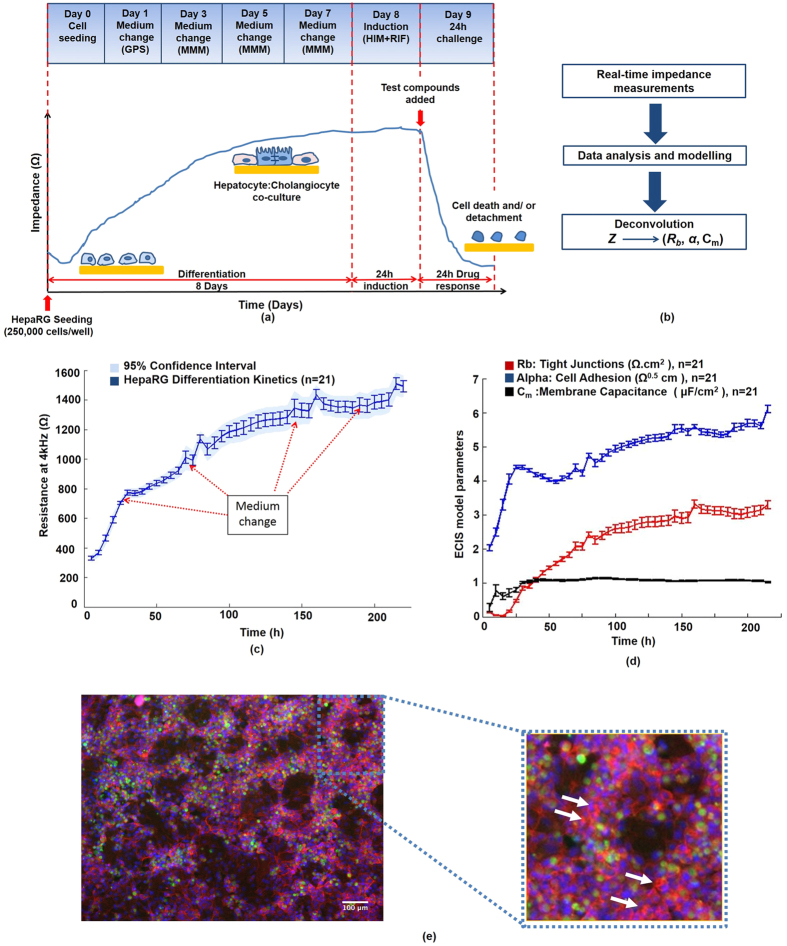
Figure 2. Establishment and characterization of human hepatic HepaRG-based model on impedance sensing arrays.
(a) Technical workflow for the human HepaRG-based liver-on-a-chip approach: HepaRG cells are seeded at high density on microelectrode arrays. The impedance, Z, is recorded in real-time throughout cell differentiation (8 days). HepaRG cells self-organize into a terminally-differentiated hepatocyte:cholangiocyte co-culture; which was mirrored by an increase in resistance at 4 kHz, indicative of tissue barrier formation. After induction, a 24 h time- and dose-response is recorded at multiple frequencies. Impedance values of cells exposed to highly toxic drug levels, can reach the value of the cell-free electrode, demonstrating complete cell death and detachment from the microelectrodes. But critically, early and low-dose effects are mainly found to disrupt hepatic adhesion structures. (b) The different current pathways are analysed using the built-in ECIS model. The impedance is then deconvolved into biologically-relevant cell electrical parameters: Rb (cell-cell junctions), z-alpha (cell-electrode adhesion) and Cm (cell membrane capacitance). (c) HepaRG differentiation kinetics: As the cell population undergoes self-organization/maturation, the resistance at 4 kHz increased steadily until reaching a plateau on day 7, reflecting completion of the differentiation/maturation phase, and epithelial polarization; as evidenced by: (d) retrieval of parameters related to barrier function (Rb), cell-substrate adhesion (z-alpha) and cell membrane capacitance (Cm)-confirming establishment of HepaRG cell-cell tight junctions, cell-electrode adhesion and stable, intact cellular membranes (Cm). (e) HepaRG cells exhibited a highly differentiated phenotype (day 8): Tri-colour fluorescent-staining revealed extensive hepatic CYP3A4 enzyme activity (green); punctate staining of F-actin bands, indicative of bile-canalicular structures (red; Phalloidin-staining; white arrows); with in vivo-like hepatic cords (H) and cholangiocyte-like cells (Ch; ‘voids’).