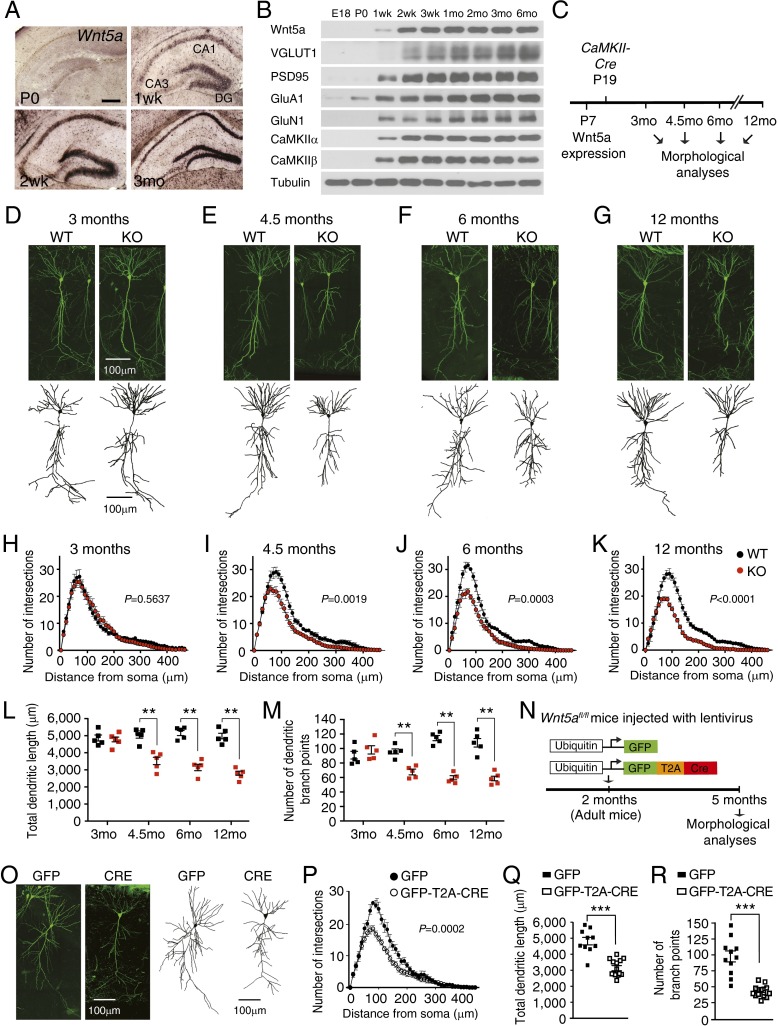
Fig. 1.
Wnt5a is required cell-autonomously for maintenance of adult CA1 dendrite architecture. (A) In situ hybridization shows Wnt5a transcript in the mouse hippocampus at postnatal stages. Wnt5a is absent at the day of birth (P0) but is detected by 1 wk and is abundant in the 3-mo-old hippocampus. (Scale bar, 300 μm.) (B) Onset of Wnt5a protein expression coincides with the appearance of pre- and postsynaptic proteins in hippocampal neurons. Hippocampal homogenates from mice of different ages (ranging from E18 to 6 mo) were immunoblotted with antibodies against Wnt5a, VGLUT1, PSD95, GluA1, GluN1, CaMKIIα, CaMKIIβ, and tubulin. (C) Schematic of the strategy to assess effects of postnatal Wnt5a deletion on neuronal morphologies in adult mice at different ages using CaMKIIα-Cre transgenic mice. (D–G) Representative images of GFP+ CA1 pyramidal neurons show that dendritic arbors are normal at 3 mo, but become progressively stunted with age in Thy1-GFP;CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl (KO) mice compared with control Thy1-GFP;Wnt5afl/fl mice (WT). (Scale bar, 100 μm.) Shown below are 3D reconstructions of neuronal soma and dendrites from WT and KO mice at 3, 4.5, 6, and 12 mo using Imaris. (H–K) Sholl analyses show that dendritic complexity is unaffected in 3-mo-old KO mice but significantly decreased by 4.5 mo and declines in older KO mice. Results are mean ± SEM from five neurons traced per animal and a total of five mice per genotype. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. (L and M) Total dendrite length and number of dendritic branch points are unaltered in 3-mo-old KO mice, but progressively decreases from 4.5 mo to 12 mo in older KO mice. Results are mean ± SEM from five neurons traced per animal and a total of five mice per genotype. **P < 0.01 two-tailed t test. (N) Wnt5afl/fl mice were stereotaxically injected with lentiviral vectors expressing GFP-T2A-CRE or GFP at 2 mo and dendritic morphologies analyzed after 3 mo. (O) Dendritic arbors were stunted in Cre-expressing neurons compared with GFP-expressing neurons. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (P) Sholl analysis shows decreased dendrite arbor complexity in sparsely labeled Cre-expressing neurons compared with controls. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. (Q and R) Dendritic lengths and branch points are reduced in Cre-expressing neurons compared with controls. Results are mean ± SEM from 14 GFP-T2A-CRE- and 10 GFP-infected neurons from a total of 10 Wnt5afl/fl mice. ***P < 0.001, two-tailed t test.