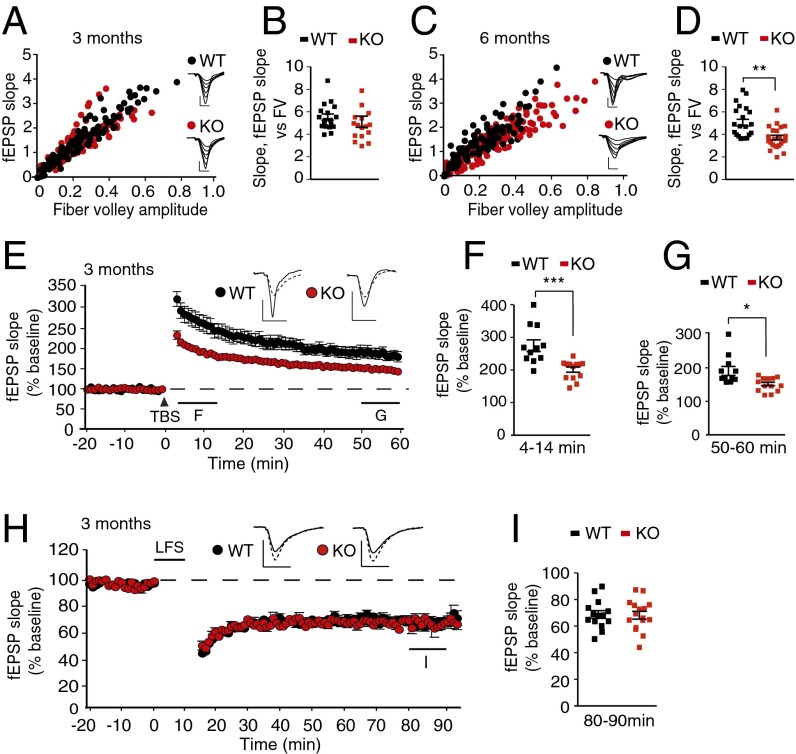
Fig. 2.
Wnt5a loss impairs LTP in the absence of changes in basal synaptic transmission or neuronal morphology. (A–D) Basal synaptic transmission is unaffected in CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl (KO) mice at 3 mo but impaired at 6 mo compared with Wnt5afl/fl litter-mates (WT). The input–output relationships and slopes of input–output curves are normal in 3-mo-old KO mice, but significantly different from WT at 6 mo. Results are mean ± SEM from five animals per genotype (n = 18 slices for WT and 17 slices for KO mice) at 3 mo, and from five WT (n = 21 slices) and four KO mice (n = 23 slices) at 6 mo. **P < 0.01, two-tailed t test. [Scale bars, 1 mV (vertical), 2.5 ms (horizontal) for all sample traces.] (E) Impaired LTP at the Schaffer collateral–CA1 synapses in 3-mo-old KO mice. n = 11 slices from 5 WT mice and n = 13 slices from 6 KO mice. Sample traces represent fEPSPs (field excitatory postsynaptic potentials) right before (dashed line) and 1 h after (solid line) θ-burst stimulation. [Scale bars, 1 mV (vertical), 10 ms (horizontal) for both sample traces.] (F and G) Induction and maintenance of LTP are attenuated in KO mice. Results are mean ± SEM from five WT mice (n = 11 slices) and six KO mice (n = 13 slices). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, two-tailed t test. (H) Low-frequency stimulation-induced LTD at Schaffer collateral–CA1 synapses is unaltered in 3-mo CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl mice. Sample traces represent fEPSPs right after (dashed line) and 1hr after (solid line) stimulation. [Scale bars, 1 mV (vertical), 10 ms (horizontal) for both sample traces.] (I) Mean fEPSP slopes are comparable between the genotypes. Results are mean ± SEM from five Wnt5afl/fl mice (n = 14 slices) and five CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl mice (n = 16 slices).