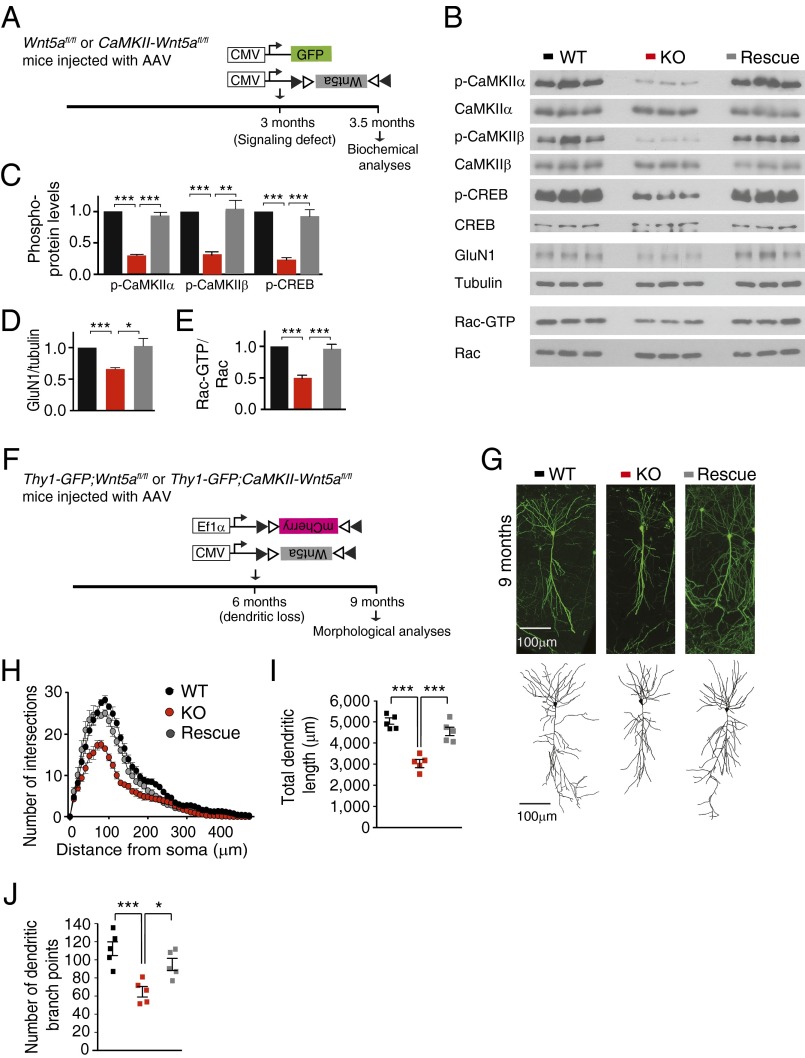
Fig. 5.
Reversal of dendritic attrition by late induction of Wnt5a expression. (A) Schematic of the strategy to assess effects of Wnt5a expression on synaptic signaling in CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl mice. Cre-dependent AAV expressing Wnt5a (AAV-DIO-Wnt5a) was injected into CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl mice at 3 mo and biochemical analyses performed 2 wk later. AAV-DIO-Wnt5a infected mutant mice (Rescue) were compared with CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl mice (KO) or control Wnt5afl/fl mice (WT) infected with AAV-GFP. (B–E) Wnt5a expression fully restored CaMKII and CREB phosphorylation, GluN1 expression, and Rac1 activity in CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl hippocampi. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 6 mice per group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. (F) Schematic of the strategy to assess effects of Wnt5a expression on neuronal morphology in adult Thy1-GFP;CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl mice. AAV-DIO-Wnt5a was delivered into Thy1-GFP;CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl hippocampus at 6 mo when there is marked dendritic regression, and morphological analyses were performed at 9 mo. Infected neurons were identified by coinfection of AAV-DIO-mCherry. GFP fluorescence was used for imaging. (G) CA1 dendritic arbors in Wnt5a-infected Thy1-GFP;CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl mice (Rescue) were comparable to control Thy1-GFP;Wnt5afl/fl mice (WT). However, Thy1-GFP;CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl neurons (KO) infected with AAV-DIO-mCherry had stunted dendritic arbors, as expected. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (H) Sholl analysis shows that AAV-mediated Wnt5a expression for 3 mo corrects dendrite complexity defects in 9-mo-old Thy1-GFP;CaMKII-Wnt5afl/fl mice. (I and J) Dendritic lengths and dendritic branch points are comparable between WT and Rescue neurons, but significantly decreased in KO neurons in 9-mo-old mice. Results are mean ± SEM from n = 5 neurons traced per animal and a total of five mice per group; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.