Figure 6. The STI‐II region of UBQLN4 determines its specificity to misassembled IL‐2Rα.
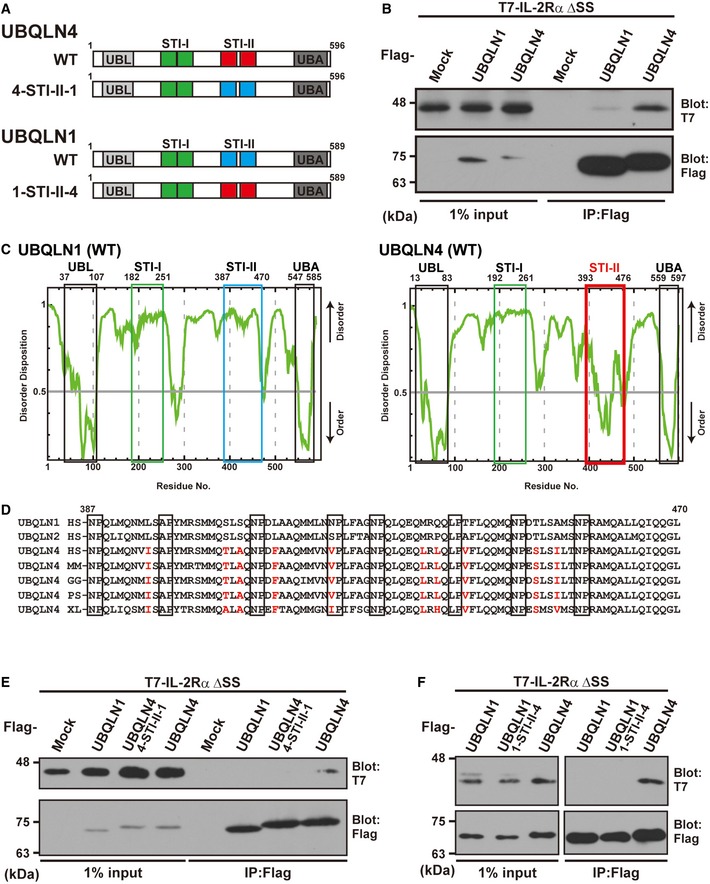
- Schematic representation of the UBQLN1, UBQLN4, and STI‐II mutant proteins used in this study.
- UBQLN4 dominantly co‐precipitates IL‐2Rα ΔSS over UBQLN1. Precipitates of Flag‐tagged UBQLN1 or UBQLN4 from HeLa cell lysates were probed with IL‐2Rα ΔSS.
- The complete amino acid sequences of human UBQLN1 and UBQLN4 were analyzed using the disorder/order structure prediction program PONDR‐FIT. The STI‐II region of UBQLN4 is indicated by the red box, and that of UBQLN1 is boxed blue. Note that the disorder tendency of the UBL, STI‐I, and UBA regions is nearly identical between UBQLN1 and UBQLN4 (indicated by black and green boxes), while that of the STI‐II region is quite distinct, and the STI‐II of UBQLN4 shows a high probability of an ordered structure. The numbers denote the corresponding amino acid positions in these proteins.
- Amino acid sequence alignments of the STI‐II regions of UBQLN1 and UBQLN4. UBQLN4‐specific residues are shown as red characters. HS: Homo sapiens (Mammalia), MM: Mus musculus (Mammalia), GG: Gallus gallus (Aves), PS: Pelodiscus sinensis (Reptilia), and XL: Xenopus laevis (Amphibia).
- Substitution of the STI‐II sequence of UBQLN4 with that of UBQLN1 (designated as the 4‐STI‐II‐1 mutant protein) abolished its high affinity to the IL‐2Rα ΔSS client protein.
- Substitution of the STI‐II sequence of UBQLN1 with that of UBQLN4 (designated as the 1‐STI‐II‐4) did not enable UBQLN1 to recognize IL‐2Rα ΔSS.
Source data are available online for this figure.
