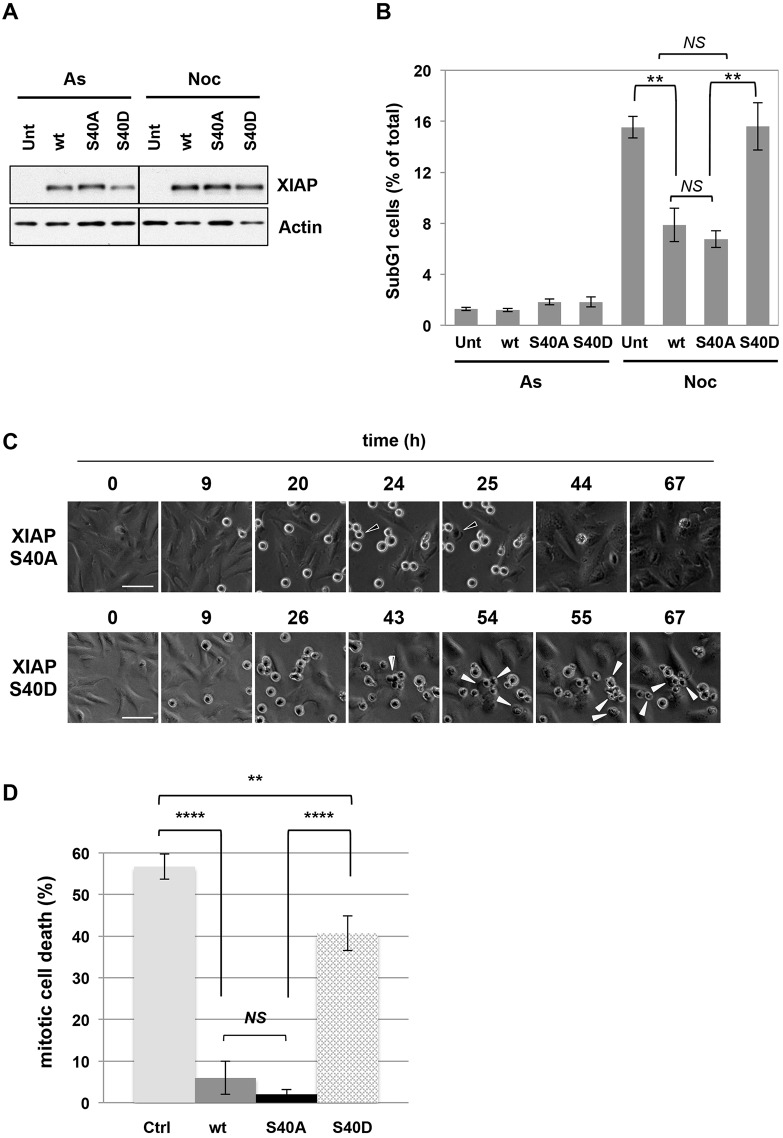
Fig. 7.
Mutation of S40 in XIAP to a phosphomimetic aspartate residue inhibits its ability to protect cells against apoptosis induced by prolonged mitotic arrest. (A,B) Cell death following mitotic arrest is not inhibited by expression of XIAP S40D protein. U2OS cells that were untransfected (Unt), stably expressing GFP-tagged wild-type (wt), S40A or S40D mutant XIAP protein were treated with 250 ng/ml nocodazole for 48 h. All cells were collected at the end of the timecourse and either (A) lysed, analysed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting (representative blots are shown) or (B) fixed and stained with propidium iodide for sub-G1 analysis using flow cytometry (n=3). In B, results are mean±s.d. **P<0.005; NS, non-significant difference (Student's unpaired t-test). (C,D) XIAP S40D fails to restrain apoptosis during mitotic arrest. Cells stably expressing GFP-tagged wild-type (wt), S40A or S40D mutant XIAP protein were treated with 250 ng/ml nocodazole. Cell fate following mitotic entry was monitored by time-lapse microscopy. (C) Representative images of cells expressing S40A or S40D mutant XIAP are shown. Examples of cells undergoing slippage (open arrows) or mitotic cell death (full arrows) are indicated. Scale bars: 50 µm. (D) Quantification of mitotic cell death in cell lines depicted in C, control cells (Ctrl) and cells expressing wild-type XIAP (wt). For each experiment (n=3), the fate of 50 cells was assessed. Results are mean±s.d. **P<0.01; ****P<0.0001; NS, non-significant difference (Student's unpaired t-test).