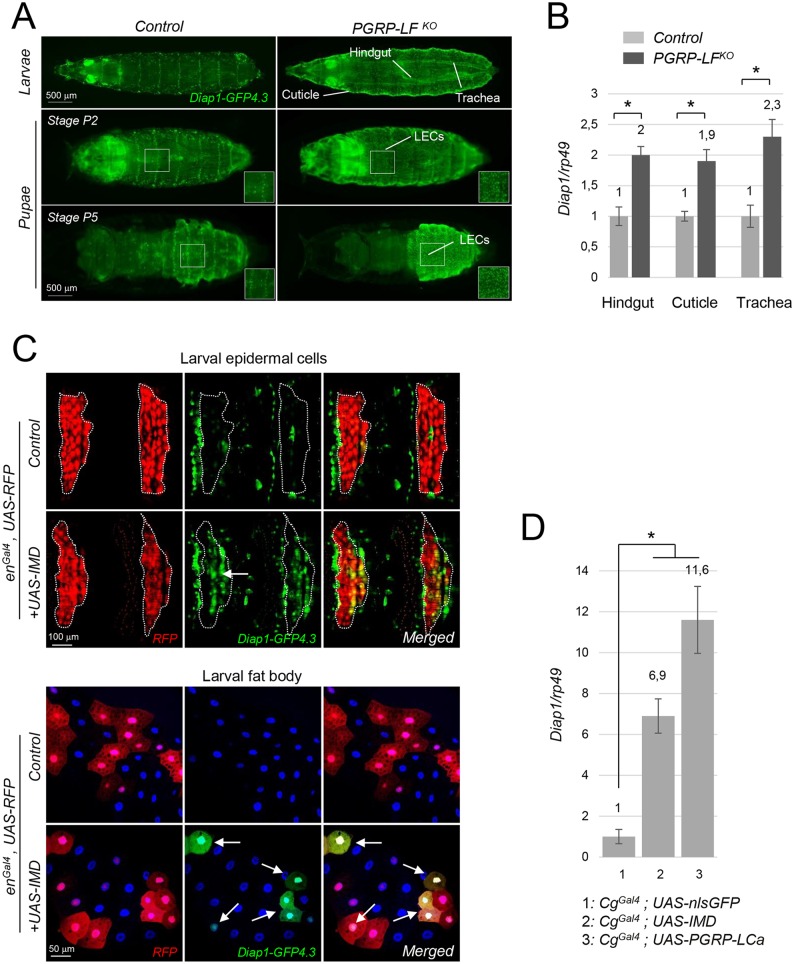
Fig 7. Activation of Diap1 expression in PGRP-LF mutants and IMD gain-of-function cells.
(A) Dorsal views of third instar larvae and pupal cases showing ectopic expression of Diap1-GFP4.3 in PGRP-LF mutant LECs, trachea and hindguts. See also S7 Fig. (B) Expression of Diap1 mRNA is higher in hindgut, trachea and cuticle from PGRP-LF mutant larvae than from controls. (C) Diap1-GFP4.3 expression is induced in cells overexpressing IMD. Dorsal epidermis (top images) and fat body (bottom images) of enGal4, UAS-RFP/+ (control) and enGal4, UAS-RFP/+; UAS-IMD/+ (UAS-IMD) larvae are shown. In LECs and fat body cells, IMD expression induce Diap1-GFP4.3 cell autonomously (arrows). (D) Expression of Diap1 mRNA is induced following overexpression of IMD and PGRP-LCa in adult fat body. Abdomen from 6d old females of the following genotypes were dissected and analyzed by q-RT-PCR: CgGal4/nlsUAS-GFP (control), CgGal4/+; UAS-IMD/+ (UAS-IMD) and CgGal4/+; UAS-PGRP-LCa/+ (UAS-PGRP-LCa). For (B) and (D) mRNA level in control was set to 1, and values obtained with tissues or larvae of indicated genotypes were expressed as a fold of this value. For (B) and (D) histograms correspond to the mean value ± SD of three independent experiments. Values indicated by symbols (*) are statistically significant (t-test, p < 0.05). ns: not significantly different.