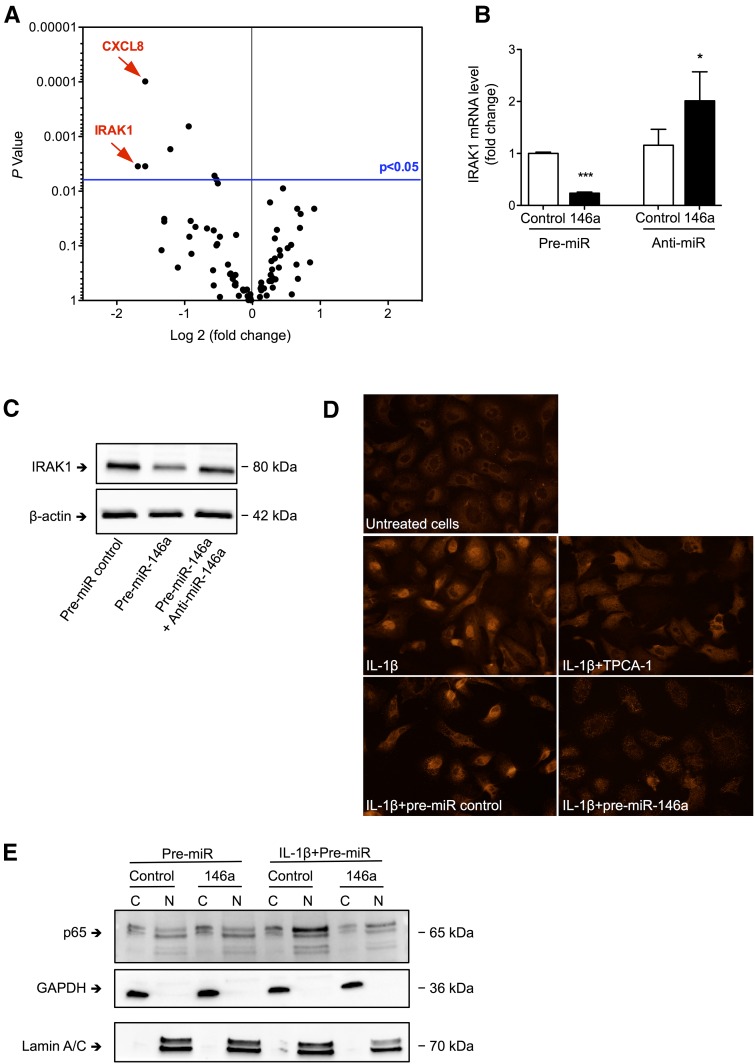
Figure 5.
miR-146a inhibits nuclear translocation of the p65 NF-κB subunit in response to IL-1β. (A) Volcano plot showing changes in the levels of 84 mRNAs related to the NF-κB pathway as detected by PCR arrays analyzing RNA from HK-2 cells transfected with pre–miR-146a or a control and incubated for 24 hours with 50 ng/ml IL-1β. (B) IRAK1 mRNA levels 24 hours after transfection of HK-2 cells with pre–miR-146a or anti–miR-146a (50 nM). Target mRNA levels were normalized to HPRT levels. (C) Western blot of IRAK1 in HK-2 cells 24 hours after transfection of HK-2 cells with pre–miR-control, pre–miR-146a, or both pre–miR-146a and anti–miR-146a (50 nM). (D) p65 NF-κB subunit immunofluorescence in control HK-2 cells incubated for 1 hour with 50 ng/ml IL-1β and 10 μM TPCA-1 or n HK-2 cells transfected with pre–miR-control or pre–miR-146a; untreated cells were used as a negative control. (E) Western blot of the p65 NF-κB subunit on nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts from HK-2 cells transfected with pre–miR-control or pre–miR-146a in the presence or absence of IL-1β; Western blots of GAPDH and lamin A/C were used to confirm the purity of the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. Data are shown as means±SEM. *P<0.05.