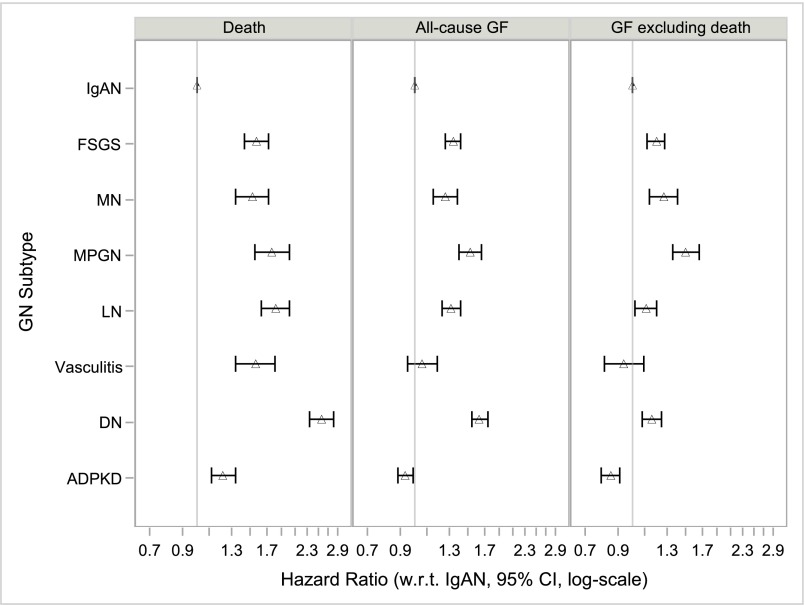
Figure 3.
Increased hazards for death and for allograft failure (including or excluding death as a cause) for comparator causes of ESRD compared to IgA nephropathy (IgAN). Model 4 (fully adjusted) HRs with 95% CIs for the primary outcomes of death, all-cause allograft failure, and allograft failure excluding death as a cause (competing risks model), by cause of ESRD, n=107,778. Model 4 stratified by year of transplantation and adjusted for age, age*age, sex, race, ethnicity, geographic region, insurance type, college education, dialysis modality, dialysis vintage, comorbidities (unable to ambulate, coronary heart disease, cancer, congestive heart failure, COPD, CVA/TIA, diabetes, hypertension, current/recent smoker, PVD), BMI group, HCV status, ABO blood group, CIT, donor age, donor sex, donor race, HLA mismatch group, donor type (living/decreased/expanded criteria), PPRA, initial post-transplant immunosuppression (Alemtuzumab, Basiliximab, Daclizumab, or Thymoglobulin induction; Tacrolimus, Ciclosporin, Sirolimus, MMF, Azathioprine and/or steroid maintenance), previous blood transfusion, and DGF. BMI, body mass index; CIT, cold ischemia time; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CVA, cerebrovascular accident; DN, diabetic nephropathy; HLA, histocompatibility leukocyte antigen; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; PPRA, peak panel reactive antibody; PVD, peripheral vascular disease; TIA, transient ischemic attack.