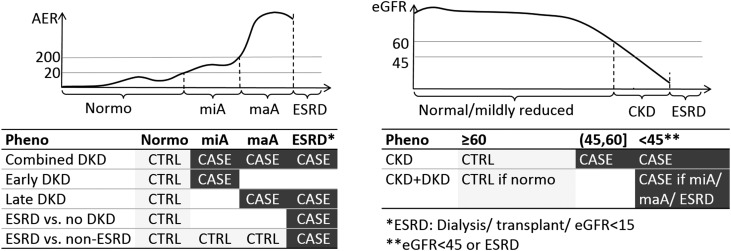
Figure 1.
Schematic picture of the DKD phenotypic comparisons on the basis of measured AER and eGFR, encompassing different stages and severities of DKD. ‘Combined DKD’ and ‘Late DKD’ (conventionally used in many previous genetic studies of DKD) are expected to capture genetic factors affecting DKD in general; ‘Early DKD’ comparison targets the genetic factors affecting the initiation of DKD, or with milder effect on the phenotype, whereas the two ESRD-based case definitions are expected to capture factors related to the late progression of DKD such as fibrotic processes, or genetic factors with particularly strong effect on the phenotype. Although the ‘CKD’ phenotype may reveal genetic factors for reduced renal function irrespective of the presence of albuminuria, the ‘CKD+DKD’ phenotype is an extreme phenotype that requires that controls have no signs of renal complications (neither AER or eGFR based). AER thresholds are given in µg/min, eGFR thresholds in ml/min per 1.73 m2. Number of samples per subphenotype: Normo: 2593; miA: 800; maA: 944; ESRD: 813; no CKD: 2909; CKD: 1255; no CKD, no DKD: 2018; CKD+DKD: 1117. Normo, normal AER; miA, microalbuminuria; maA, macroalbuminuria.