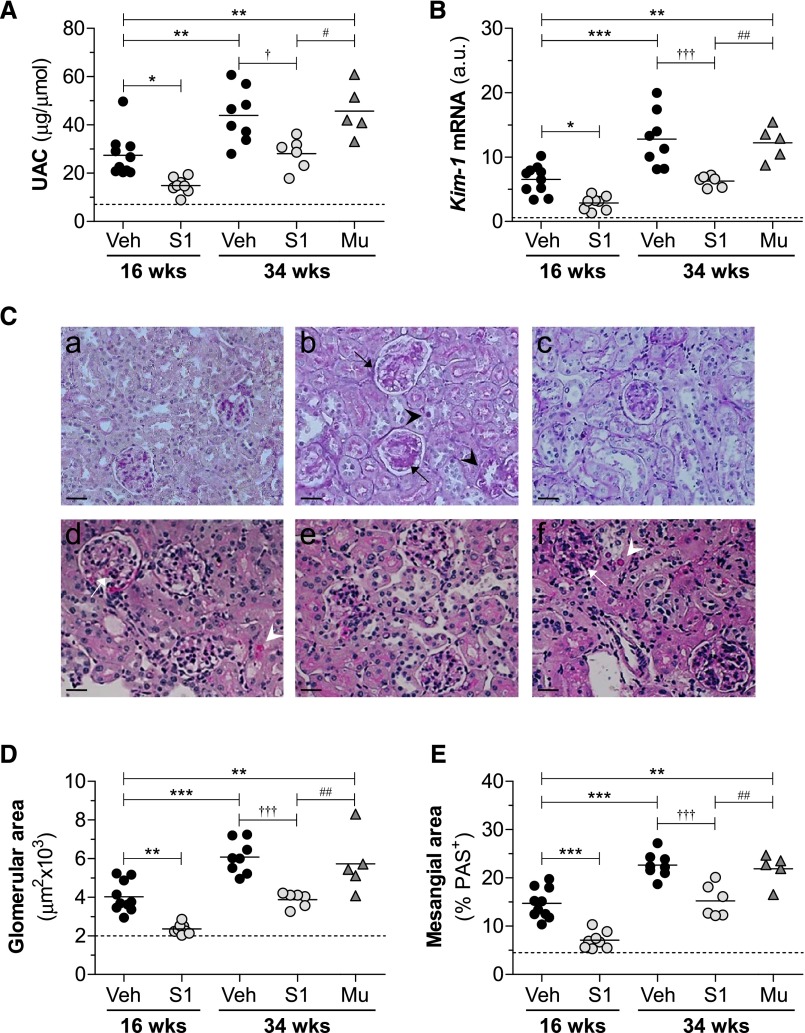
Figure 2.
SOCS1 peptide protects from diabetes-associated renal injury in apoE-deficient mice. (A) Albuminuria levels in apoE-deficient mice at early (age 16 weeks) and late (age 34 weeks) diabetes. (B) Gene expression of kidney injury molecule (Kim-1) in renal cortex was analyzed by real-time PCR, normalized by 18S endogenous control, and expressed in arbitrary units (a.u.). (C) Representative images of PAS-stained kidney sections from mice in the early (age 16 weeks; a–c) and late (age 34 weeks; d–f) diabetes models: nondiabetes (a), diabetes+vehicle (b and d), diabetes+S1 (c and e), and diabetes+Mu (f). Diabetic mice exhibited glomerular hypertrophy/PAS+ area expansion (arrows) and tubular atrophy/glycogen deposition (arrowheads). Milder damage was observed in S1 groups. (D) Glomerular area quantification in the experimental groups. (E) PAS+ mesangial area analysis. Veh, vehicle. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 versus Veh (16 weeks); †P<0.05 and †††P<0.001 versus Veh (34 weeks); #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01 versus Mu. Horizontal dotted lines represent the mean values for nondiabetic mice in A, B, D, and E. Original magnification, ×200 in C.