Figure 1.
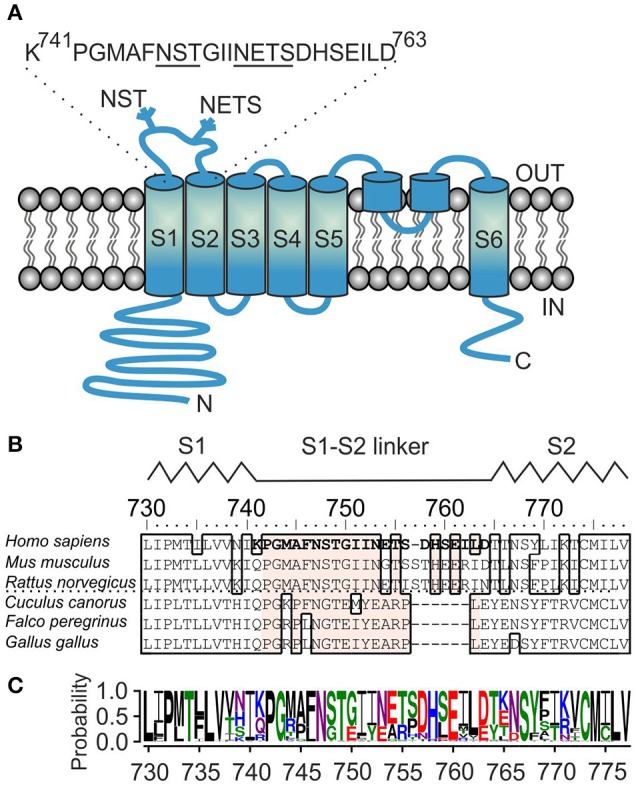
Sequence analysis of the S1–S2 linker region of TRPA1 channel. (A) Schematic illustration of human TRPA1 subunit with depicted position and sequence of S1–S2 linker, beginning with P742 and G743, and containing two glycosylation consensus sites 747NST and 753NETS (underlined). The extracellularly and intracellularly oriented part of the protein forms, respectively, the “upper part” and the “lower part” of the channel. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of S1–S2 linkers from representative TRPA1 protein orthologs. The residues mutated in this study are indicated in bold type. Conserved residues inside the S1–S2 linker across TRPA1 orthologs are depicted in beige. The interrupted line indicates sequential differences between human, rodent and bird TRPA1. Interspecies diversity from 752 to 771. The schematic location of the S1–S2 linker between the S1 and S2 helices of human TRPA1 is indicated above the alignment. (C) Amino-acid sequence conservation within S1–S2 linker of 57 TRPA1 proteins represented as sequence logo generated using WebLogo server (Crooks et al., 2004). The height of the particular amino acid at each position indicates its probability of occurance at that position. P742, G743, and N747 are conserved unanimously.
