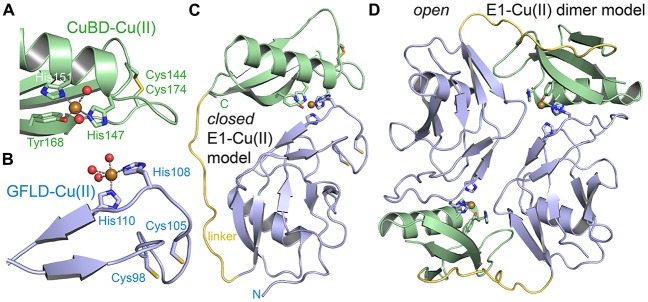
Figure 2.
Metal binding to the E1 domain. (A) The CuBD of human APP bound to copper (II) (PDB code: 2fk1). Copper is coordinated by three protein ligands and two water molecules. The shown disulfide bridge is partially reduced. (B) The GFLD of human APP bound to copper (II) (PDB code: 4jfn). Copper is coordinated in the same geometry as in the CuBD. Two ligand sites are occupied by protein and three sites by a crystal contact (aspartate) replacing three water molecules. The inferred hydrated state in solution is shown. The disulfide bridge adjacent to the copper binding site is reduced. (C) A putative “closed” E1 domain by the intramolecular combination of the two ligand bindings sites of GFLD and CuBD and modeling of a flexible linker (yellow). (D) The respective “open” E1 domain by intermolecular combination of the binding sites. The monomeric E1 domain corresponds to PDB code 4pwq.